Glycine Transporter 1 Inhibitors Minimize the Analgesic Tolerance to Morphine
- PMID: 39456918
- PMCID: PMC11508341
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011136
Glycine Transporter 1 Inhibitors Minimize the Analgesic Tolerance to Morphine
Abstract
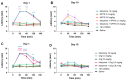
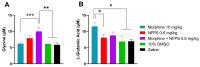
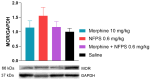
Opioid analgesic tolerance (OAT), among other central side effects, limits opioids' indispensable clinical use for managing chronic pain. Therefore, there is an existing unmet medical need to prevent OAT. Extrasynaptic N-methyl D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) containing GluN2B subunit blockers delay OAT, indicating the involvement of glutamate in OAT. Glycine acts as a co-agonist on NMDARs, and glycine transporters (GlyTs), particularly GlyT-1 inhibitors, could affect the NMDAR pathways related to OAT. Chronic subcutaneous treatments with morphine and NFPS, a GlyT-1 inhibitor, reduced morphine antinociceptive tolerance (MAT) in the rat tail-flick assay, a thermal pain model. In spinal tissues of rats treated with a morphine-NFPS combination, NFPS alone, or vehicle-comparable changes in µ-opioid receptor activation, protein and mRNA expressions were seen. Yet, no changes were observed in GluN2B mRNA levels. An increase was observed in glycine and glutamate contents of cerebrospinal fluids from animals treated with a morphine-NFPS combination and morphine, respectively. Finally, GlyT-1 inhibitors are likely to delay MAT by mechanisms relying on NMDARs functioning rather than an increase in opioid efficacy. This study, to the best of our knowledge, shows for the first time the impact of GlyT-1 inhibitors on MAT. Nevertheless, future studies are required to decipher the exact mechanisms.
Keywords: NFPS; NMDARs; glycine transporter-1; opioid analgesic tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Glycine transporter inhibitors: A new avenue for managing neuropathic pain.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Oct;152:143-158. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.07.008. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 31302238 Review.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling mediates opioid-induced presynaptic NMDA receptor activation and analgesic tolerance.J Neurochem. 2019 Jan;148(2):275-290. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14628. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 30444263 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the glycine transporter GlyT-1 potentiates the effect of risperidone, but not clozapine, on glutamatergic transmission in the rat medial prefrontal cortex.Synapse. 2006 Aug;60(2):102-8. doi: 10.1002/syn.20286. Synapse. 2006. PMID: 16715496
-
Pharmacological Evidence on Augmented Antiallodynia Following Systemic Co-Treatment with GlyT-1 and GlyT-2 Inhibitors in Rat Neuropathic Pain Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 1;22(5):2479. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052479. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804568 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine Transporter 1 Inhibitors: Predictions on Their Possible Mechanisms in the Development of Opioid Analgesic Tolerance.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 12;12(2):421. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020421. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial to the Special Issue "Glycine-(and D-Serine)-Related Neurotransmission: Promising Therapeutic Targets with Still Unsolved Problems".Biomedicines. 2025 May 8;13(5):1140. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051140. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426967 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FK_138389/Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the Na-tional Research, Development and Innovation Fund
- TKP 2021 EGA-25/Higher Education Institutional Excellence Programme of the Ministry of Human Capacities in Hungary, within the framework of the Neurology Thematic Programme of Semmelweis University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

