Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Predictor of Treatment Response in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39456983
- PMCID: PMC11508575
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011204
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Predictor of Treatment Response in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a potential biomarker of response to treatment in psychiatric disorders. As it plays a role in the pathophysiological development of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, it is of interest to study its role in predicting therapeutic responses in both conditions. We carried out a systematic review of the literature, looking for differences in baseline BDNF levels and the Val66Met BDNF polymorphism in these disorders between responders and non-responders, and found information showing that the Val/Val genotype and higher baseline BDNF levels may be present in patients that respond successfully to pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments. However, there is still limited evidence to support the role of the Val66Met polymorphism and baseline BDNF levels as predictors of treatment response.
Keywords: BDNF; biomarkers; bipolar disorder; neurotrophins; schizophrenia; treatment refractoriness; treatment resistance; treatment response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
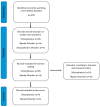
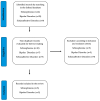
References
-
- Gao K., Ayati M., Koyuturk M., Calabrese J.R., Ganocy S.J., Kaye N.M., Lazarus H.M., Christian E., Kaplan D. Protein Biomarkers in Monocytes and CD4+ Lymphocytes for Predicting Lithium Treatment Response of Bipolar Disorder: A Feasibility Study with Tyramine-Based Signal-Amplified Flow Cytometry. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 2022;52:8–35. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

