Hybrid Albumin-Decorated Lipid-Nanocarrier-Mediated Delivery of Polyphenol-Rich Sambucus nigra L. in a Potential Multiple Antitumoural Therapy
- PMID: 39456987
- PMCID: PMC11508305
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011206
Hybrid Albumin-Decorated Lipid-Nanocarrier-Mediated Delivery of Polyphenol-Rich Sambucus nigra L. in a Potential Multiple Antitumoural Therapy
Abstract
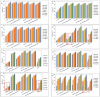
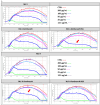
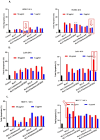
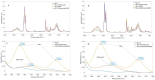
The current research attempted to address the suitability of bioactive Sambucus nigra extract entrapped in albumin-decorated nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) as a promising "adjuvant" in improving tumour penetration for multiple antitumour therapy. The new hybrid albumin-decorated NLCs were characterised based on, e.g., the particle size, zeta electrokinetic potential, SambucusN entrapment efficiency, and fluorescence spectroscopy and tested for different formulation parameters. The antioxidant activity of NLC-SambucusN was significantly enhanced by a bovine serum albumin (BSA) polymer coating. According to the real-time cell analysis (RTCA) results, NLC-I-SambucusN-BSA behaved similarly to the chemotherapeutic drug, cisplatin, with cell viability for LoVo tumour cells of 21.81 ± 1.18%. The new albumin-NLC-SambucusN arrested cancer cells in G1 and G2 cycles and intensified the apoptosis process in both early and late phases. An advanced induction, over 50% apoptosis in LoVo colon cells, was registered for 50 μg/mL of NLC-II-SambucusN-BSA, a fourfold increase compared to that of untreated cells. RTCA and flow cytometry results showed that concentrations of the hybrid NLC-SambucusN up to 50 μg/mL do not affect the proliferation of normal HUVEC cells. This approach provides insightful information regarding the involvement of phytochemicals in future therapeutic strategies. Albumin-decorated NLCs can be considered a noteworthy strategy to be connected to antitumour therapeutic protocols.
Keywords: Sambucus -nigra; antioxidant effect; apoptosis process; cell cycle arrest; phytochemical entrapment; protein–lipid nanocarriers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Novel Bovine Serum Albumin-Decorated-Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Able to Modulate Apoptosis and Cell-Cycle Response in Ovarian, Breast, and Colon Tumoral Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 2;15(4):1125. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041125. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111611 Free PMC article.
-
The anticancer impact of folate-linked ZnO-decorated bovine serum albumin/silibinin nanoparticles on human pancreatic, breast, lung, and colon cancers.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2024 Aug;35(12):1845-1862. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2024.2356967. Epub 2024 May 29. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2024. PMID: 38809850
-
Resveratrol: Isolation, and Its Nanostructured Lipid Carriers, Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Induces Cell Apoptosis in Certain Human Cell Lines Carcinoma and Exerts Protective Effect Against Paraquat-Induced Hepatotoxicity.J Med Food. 2021 Jan;24(1):89-100. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2019.0286. Epub 2020 Jun 22. J Med Food. 2021. PMID: 32580673
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers employing polyphenols as promising anticancer agents: Quality by design (QbD) approach.Int J Pharm. 2017 Jun 30;526(1-2):506-515. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.04.078. Epub 2017 May 11. Int J Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28502895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer nano-delivery systems based on bovine serum albumin nanoparticles: A critical review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 15;193(Pt A):528-540. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.040. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34655592 Review.
References
-
- Patel A., Redingerd N., Richter A., Woods A., Neumann P.R., Keegan G., Childerhouse N., Imming P., Schaible U.E., Forbesa B., et al. In vitro and in vivo antitubercular activity of benzothiazinone-loaded human serum albumin nanocarriers designed for inhalation. J. Control. Release. 2020;328:339–349. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.08.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liang X., Mu M., Chen B., Chuan D., Zhao N., Fan R., Tang X., Chen H., Han B., Guo G. BSA-assisted synthesis of nanoreactors with dual pH and glutathione responses for ferroptosis and photodynamic synergistic therapy of colorectal cancer. Mater. Today Adv. 2022;16:100308. doi: 10.1016/j.mtadv.2022.100308. - DOI
-
- Cao H., Zou L., He B., Zeng L., Huang Y., Yu H., Zhang P., Yin Q., Zhang Z., Li Y. Albumin biomimetic nanocorona improves tumor targeting and penetration for synergistic therapy of metastatic breast cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017;27:1605679. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201605679. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

