Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as Carrier of Pro-Apoptotic Oncolytic Myxoma Virus: To Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier and Treat Murine Glioma
- PMID: 39457007
- PMCID: PMC11508294
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011225
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as Carrier of Pro-Apoptotic Oncolytic Myxoma Virus: To Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier and Treat Murine Glioma
Abstract
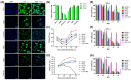
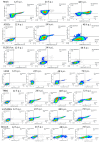
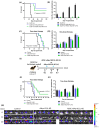
Treatment of glioblastoma is ineffective. Myx-M011L-KO/EGFP, a myxoma virus actively inducing apoptosis in BTICs linked to recurrence, offers innovative treatment. We loaded this construct into adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) to mitigate antiviral host responses and enable systemic delivery. The apoptotic and cytotoxic effects of the construct were studied using murine and human glioblastoma cell lines. Before implementing systemic delivery, we delivered the construct locally using ADSC to verify elimination of orthotopic murine glioma lesions. vMyx-M011L-KO/EGFP was cytotoxic to a murine cell line, preventing effective virus multiplication. In three human glioma cell lines, viral replication did occur, coupled with cell killing. The knock-out construct induced apoptotic cell death in these cultures. ADSCs infected ex vivo were shown to be sufficiently migratory to assure transfer of the therapeutic cargo to murine glioma lesions. Virus-loaded ADSCs applied to the artificial blood-brain barrier (BBB) yielded viral infection of glioma cells grown distally in the wells. Two rounds of local administration of this therapeutic platform starting 6 days post tumor implantation slowed down growth of orthotopic lesions and improved survival (total recovery < 20%). ADSCs infected ex vivo with vMyx-M011L-KO/EGFP show promise as a therapeutic tool in systemic elimination of glioma lesions.
Keywords: adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs); blood–brain barrier; glioblastoma; myxoma virus; oncolytic virotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pisklakova A., McKenzie B., Zemp F., Lun X., Kenchappa R.S., Etame A.B., Rahman M.M., Reilly K., Pilon-Thomas S., McFadden G., et al. M011L-deficient oncolytic myxoma virus induces apoptosis in brain tumor-initiating cells and enhances survival in a novel immunocompetent mouse model of glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. 2016;8:1088–1098. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

