A Selective Melatonin 2 Receptor Agonist, IIK7, Relieves Blue Light-Induced Corneal Damage by Modulating the Process of Autophagy and Apoptosis
- PMID: 39457025
- PMCID: PMC11508435
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011243
A Selective Melatonin 2 Receptor Agonist, IIK7, Relieves Blue Light-Induced Corneal Damage by Modulating the Process of Autophagy and Apoptosis
Abstract
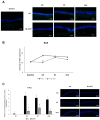
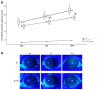
This study aims to investigate the effect of the selective MT2 receptor agonist, IIK7, on corneal autophagy and apoptosis, aiming to reduce corneal epithelial damage and inflammation from blue light exposure in mice. Eight-week-old C57BL/6 mice were divided into BL-exposed (BL) and BL-exposed with IIK7 treatment (BL + IIK7 group). Mice underwent blue light exposure (410 nm, 100 J) twice daily with assessments at baseline and on days 3, 7, and 14. Corneal samples were analyzed for MT2 receptor expression, autophagy markers (LC3-II and p62), and apoptosis indicators (BAX expression and TUNEL assay). Then, mice were assigned to normal control, BL, and BL + IIK7. Ocular surface parameters, including corneal fluorescein staining scores, tear volume, and tear film break-up time, were evaluated on days 7 and 14. On day 14, reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and CD4+ IFN-γ+ T cells percentages were measured. The BL group exhibited higher LC3-II and p62 expression, while the BL + IIK7 group showed reduced expression (p < 0.05). The TUNEL assay showed reduced apoptosis in the BL + IIK7 group compared to the BL group. ROS levels were lower in the BL + IIK7 group. The BL + IIK7 group showed improved ocular surface parameters, including decreased corneal fluorescein staining and increased tear volume. The percentages of CD4+ IFN-γ+ T cells indicated reduced inflammatory responses in the BL + IIK7 group. The MT2 receptor agonist IIK7 regulates corneal autophagy and apoptosis, reducing corneal epithelial damage and inflammation from blue light exposure.
Keywords: IIK7; apoptosis; autophagy; blue light; corneal damage; melatonin type 2 receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Melatonin Type 2 Receptor Activation Regulates Blue Light Exposure-Induced Mouse Corneal Epithelial Damage by Modulating Impaired Autophagy and Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 26;23(19):11341. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911341. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232639 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effect of Rebamipide Eye Drops on Blue Light-Induced Oxidative Damage in the Ocular Surface.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Aug;41(6):314-321. doi: 10.1089/jop.2024.0208. Epub 2025 Apr 28. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40293740
-
Blue Light Induces Impaired Autophagy through Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain 2 Activation on the Mouse Ocular Surface.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 18;22(4):2015. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042015. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670592 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress to the cornea, changes in corneal optical properties, and advances in treatment of corneal oxidative injuries.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:591530. doi: 10.1155/2015/591530. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 25861412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review of experimental models for investigating blue light-induced ocular damage: Insights into parameters, limitations, and new opportunities.Exp Eye Res. 2024 Dec;249:110142. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2024.110142. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Exp Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 39490726 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Therapeutic Effects of Rebamipide and Diquafosol on Apoptotic Damage of the Ocular Surface in Dry Eyes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 25;14(7):780. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070780. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cougnard-Gregoire A., Merle B.M.J., Aslam T., Seddon J.M., Aknin I., Klaver C.C.W., Garhöfer G., Layana A.G., Minnella A.M., Silva R., et al. Blue Light Exposure: Ocular Hazards and Prevention—A Narrative Review. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2023;12:755–788. doi: 10.1007/s40123-023-00675-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee J.-B., Kim S.-H., Lee S.-C., Kim H.-G., Ahn H.-G., Li Z., Yoon K.C. Blue Light–Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells: Protective Effects of Ethanol Extracts of Various Medicinal Plant Mixtures. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014;55:4119–4127. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13441. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BCRI22016 and BCRI23037/Chonnam National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute
- 2022R1F1A1075034 and RS-2023-00280734/Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education
- RS-2020-KH088567/Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

