Phylogenomic Analysis and Functional Characterization of the APETALA2/Ethylene-Responsive Factor Transcription Factor Across Solanaceae
- PMID: 39457030
- PMCID: PMC11508751
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011247
Phylogenomic Analysis and Functional Characterization of the APETALA2/Ethylene-Responsive Factor Transcription Factor Across Solanaceae
Abstract
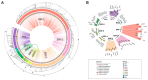
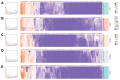
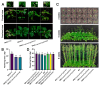
The AP2/ERF family constitutes one of the largest groups of transcription factors in the Solanaceae. AP2/ERF contributes to various plant biological processes, including growth, development, and responses to various stresses. The origins and functional diversification of AP2/ERF within the Solanaceae family remain poorly understood, primarily because of the complex interactions between whole-genome duplications (WGDs) and tandem duplications. In this study, a total of 1282 AP2/ERF proteins are identified from 7 Solanaceae genomes. The amplification of AP2/ERF genes was driven not only by WGDs but also by the presence of clusters of tandem duplicated genes. The conservation of synteny across different chromosomes provides compelling evidence for the impact of the WGD event on the distribution pattern of AP2/ERF genes. Distinct expression patterns suggest that the multiple copies of AP2/ERF genes evolved in different functional directions, catalyzing the diversification of roles among the duplicated genes, which was of great significance for the adaptability of Solanaceae. Gene silencing and overexpression assays suggest that ERF-1 members' role in regulating the timing of floral initiation in C. annuum. Our findings provide insights into the genomic origins, duplication events, and function divergence of the Solanaceae AP2/ERF.
Keywords: AP2/ERF; Solanaceae; flowering time; gene duplications; phylogenomics; synteny.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative and expression analyses of AP2/ERF genes reveal copy number expansion and potential functions of ERF genes in Solanaceae.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Jan 23;23(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-04017-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36683040 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide investigation and expression profiling of AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.).PLoS One. 2014 Nov 19;9(11):e113092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113092. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25409524 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of the Quinoa AP2/ERF gene family and their expression patterns in response to salt stress.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 27;14(1):29529. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81046-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39604476 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Events of Rice AP2/ERF Transcription Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12013. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912013. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERF Gene Clusters: Working Together to Regulate Metabolism.Trends Plant Sci. 2021 Jan;26(1):23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2020.07.015. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Trends Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 32883605 Review.
References
-
- Stockinger E.J., Gilmour S.J., Thomashow M.F. Arabidopsis thaliana Cbf1 Encodes an Ap2 Domain-Containing Transcriptional Activator That Binds to the C-Repeat/Dre, a Cis-Acting DNA Regulatory Element That Stimulates Transcription in Response to Low Temperature and Water Deficit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1997;94:1035–1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.3.1035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rasul I., Zafar F., Ali M.A., Nadeem H., Siddique M.H., Shahid M., Ashfaq U.A., Azeem F. Genetic Basis for Biotic Stress Resistance in Plants from Solanaceae Family: A Review. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019;22:178–194.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

