Antiphospholipid Antibodies as Key Players in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Relationship with Cytokines and Immune Dysregulation
- PMID: 39457063
- PMCID: PMC11509045
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011281
Antiphospholipid Antibodies as Key Players in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Relationship with Cytokines and Immune Dysregulation
Abstract
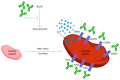
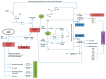
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by an overproduction of cytokines, such as interleukins and interferons, contributing to systemic inflammation and tissue damage. Antiphospholipid syndrome is a thrombo-inflammatory autoimmune disease affecting a third of SLE patients. We performed an in-depth analysis of the available literature, and we highlighted the complex interplay between immunity, inflammation, and thrombosis, the three major pathogenic pathways that are trapped in a mutually reinforcing destructive loop.
Keywords: antiphospholipid antibodies; antiphospholipid syndrome; immunity; inflammation; systemic lupus erythematosus; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hughes G.R. The Anticardiolipin Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1985;3:285–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

