Geldanamycins: Potent Hsp90 Inhibitors with Significant Potential in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 39457075
- PMCID: PMC11509085
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011293
Geldanamycins: Potent Hsp90 Inhibitors with Significant Potential in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
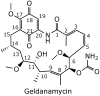
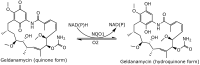
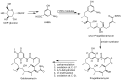
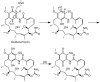
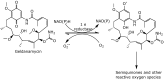
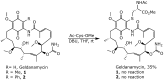
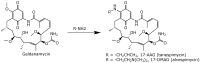
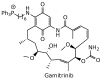
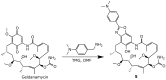
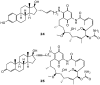
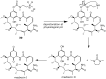
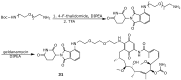
Geldanamycin, an ansa-macrolide composed of a rigid benzoquinone ring and an aliphatic ansa-bridge, was isolated from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Geldanamycin is a potent heat shock protein inhibitor with remarkable antiproliferative activity. However, it shows pronounced hepatotoxicity in animal models and unfavorable pharmacokinetic properties. Four geldanamycin analogs have progressed through various phases of clinical trials, but none have yet completed clinical evaluation or received FDA approval. To enhance the efficacy of these Hsp90 inhibitors, strategies such as prodrug approaches or nanocarrier delivery systems could be employed to minimize systemic and organ toxicity. Furthermore, exploring new drug combinations may help overcome resistance, potentially improving therapeutic outcomes. This review discusses the mechanism of action of geldanamycin, its pharmacokinetic properties, and the various approaches employed to alleviate its toxicity and maximize its clinical efficacy. The main focus is on those derivatives that have progressed to clinical trials or that have shown important in vivo activity in preclinical models.
Keywords: Hsp90; PROTAC; ansamycin; cancer; geldanamycin; mutasynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


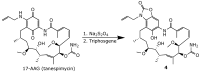



References
-
- Avendaño C., Menéndez J.C. Chapter 14—Miscellaneous small-molecule and biological approaches to targeted cancer therapy. In: Avendaño C., Menéndez J.C., editors. Medicinal Chemistry of Anticancer Drugs. 3rd ed. Elsevier; Boston, MA, USA: 2023. pp. 743–822.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

