Role of Circulating microRNAs in Liver Disease and HCC: Focus on miR-122
- PMID: 39457437
- PMCID: PMC11507253
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15101313
Role of Circulating microRNAs in Liver Disease and HCC: Focus on miR-122
Abstract
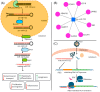
miR-122 is the most abundant microRNA (miRNA) in the liver; it regulates several genes mainly involved in cell metabolism and inflammation. Host factors, diet, metabolic disorders and viral infection promote the development of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The downregulation of miR-122 in tissue is a common feature of the progression of liver injury. In addition, the release of miR-122 in the bloodstream seems to be very promising for the early diagnosis of both viral and non-viral liver disease. Although controversial data are available on the role of circulating miR-122 as a single biomarker, high diagnostic accuracy has been observed using miR-122 in combination with other circulating miRNAs and/or proteins. This review is focused on comprehensively summarizing the most recent literature on the potential role of circulating miR-122, and related molecules, as biomarker(s) of metabolic liver diseases, hepatitis and HCC.
Keywords: HBV; HCC; HCV; NAFLD; diagnostic biomarkers; liver disease; miR-122; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Faramin Lashkarian M., Hashemipour N., Niaraki N., Soghala S., Moradi A., Sarhangi S., Hatami M., Aghaei-Zarch F., Khosravifar M., Mohammadzadeh A., et al. MicroRNA-122 in Human Cancers: From Mechanistic to Clinical Perspectives. Cancer Cell Int. 2023;23:29. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02868-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

