Advancements in Pharmacological Interventions and Novel Therapeutic Approaches for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- PMID: 39457513
- PMCID: PMC11505100
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12102200
Advancements in Pharmacological Interventions and Novel Therapeutic Approaches for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
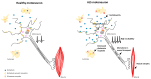
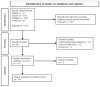
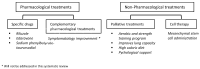
(1) Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease in which the patient suffers from an affection of both upper and lower motor neurons at the spinal and brainstem level, causing a progressive paralysis that leads to the patient's demise. Gender is also considered a predisposing risk factor for developing the disease. A brief review of the pathophysiological mechanisms of the disease is also described in this work. Despite the fact that a cure for ALS is currently unknown, there exists a variety of pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies that can help reduce the progression of the disease over a certain period of time and alleviate symptoms. (2) We aim to analyze these pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies through a systematic review. A comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to treatment is necessary. (3) Drugs such as riluzole, edaravone, and sodium phenylbutyrate, among others, have been investigated. Additionally, it is important to stay updated on research on new drugs, such as masitinib, from which very good results have been obtained. (4) Therapies aimed at psychological support, speech and language, and physical therapy for the patient are also available, which increase the quality of life of the patients.
Keywords: ALS; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; motor neuron dysfunction; multidisciplinary treatment; neurodegenerative disorder; pharmacological interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hulisz D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Disease state overview. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2018;24:S320–S326. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous