Treatment of Parkinson's Disease Psychosis-A Systematic Review and Multi-Methods Approach
- PMID: 39457629
- PMCID: PMC11505035
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12102317
Treatment of Parkinson's Disease Psychosis-A Systematic Review and Multi-Methods Approach
Abstract
Objectives: Parkinson's disease psychosis (PDP) is a prevalent non-motor symptom associated with Parkinson's disease. The treatment options for PDP are limited, and its pharmacological management remains ambiguous. This study aimed to evaluate the existing evidence in relation to clinical practice.
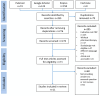
Methods: This multi-methods study consisted of a systematic review of reviews, adhering to the PRISMA guidelines. The review was registered with PROSPERO. Following data extraction and assessment using the AMSTAR 2 tool, a narrative synthesis was performed. In the second phase of the study, a questionnaire was developed, validated, piloted, and distributed to the heads of specialized PD clinics in Germany and Austria.
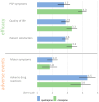
Results: The search resulted in the inclusion of eleven reviews. The quality of eight of these reviews was rated as high (n = 7) or moderate (n = 1). The reviews indicated that clozapine and pimavanserin demonstrated the highest efficacy and tolerability. Other antipsychotic medications either failed to alleviate PDP symptoms or resulted in distinct motor complications. The survey findings also favored clozapine for its efficacy in managing PDP and improving quality of life, although quetiapine was regarded as effective and pimavanserin was not available. Clinicians reported initiating antipsychotic treatment at various stages of PDP, with a tendency to reduce the dosage or discontinue D2 agonists or anticholinergics.
Conclusions: The reviewed literature and the survey results consistently favored clozapine for its efficacy and tolerability in treating PDP. It may be considered the first-line treatment, with pimavanserin as an alternative option.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease psychosis; clozapine; multi-methods; pharmacotherapy; pimavanserin; quetiapine; survey; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rose O. Parkinson-Krankheit: Basiswissen. Med. Monatsschrift Pharm. 2016;39:277–281. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

