Blast Transformation of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Driven by Acquisition of t(8;21)(q22;q22)/ RUNX1::RUNX1T1: Selecting Optimal Treatment Based on Clinical and Molecular Findings
- PMID: 39457651
- PMCID: PMC11504412
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12102339
Blast Transformation of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Driven by Acquisition of t(8;21)(q22;q22)/ RUNX1::RUNX1T1: Selecting Optimal Treatment Based on Clinical and Molecular Findings
Abstract
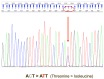
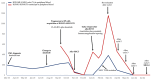
The advent of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has changed the natural history of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), and the transformation from the chronic phase to the blast phase (BP) is currently an uncommon situation. However, it is one of the major remaining challenges in the management of this disease, as it is associated with dismal outcomes. We report the case of a 63-year-old woman with a history of CML with poor response to imatinib who progressed to myeloid BP-CML, driven by the acquisition of t(8;21)(q22;q22)/RUNX1::RUNX1T1. The patient received intensive chemotherapy and dasatinib, followed by allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). However, she suffered an early relapse after allo-HSCT with the acquisition of the T315I mutation in ABL1. Ponatinib and azacitidine were started as salvage treatment, allowing for the achievement of complete remission with deep molecular response after five cycles. Advances in the knowledge of disease biology and clonal evolution are crucial for optimal treatment selection, which ultimately translates into better patient outcomes.
Keywords: T315I mutation; blast phase; chronic myeloid leukemia; core binding factor rearrangement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transformation into acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21)(q22;q22.1); RUNX1::RUNX1T1 from JAK2-mutated essential thrombocythemia: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Aug 18;18(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04691-0. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39154170 Free PMC article.
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can improve the prognosis of high-risk pediatric t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia in first remission based on MRD-guided treatment.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jun 15;20(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07043-5. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32539815 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pre- and post-transplant ponatinib for a patient with acute megakaryoblastic blast phase chronic myeloid leukemia with T315I mutation who underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Int J Hematol. 2019 Jul;110(1):119-123. doi: 10.1007/s12185-019-02628-8. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Int J Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30879266
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2025 update on diagnosis, therapy, and monitoring.Am J Hematol. 2024 Nov;99(11):2191-2212. doi: 10.1002/ajh.27443. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Am J Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39093014 Review.
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring.Am J Hematol. 2018 Mar;93(3):442-459. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25011. Am J Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29411417 Review.
References
-
- Hochhaus A., Burchert A., Saussele S., Baerlocher G.M., Mayer J., Brümmendorf T.H., La Rosée P., Heim D., Krause S.W., le Coutre P., et al. Treatment free remission after nilotinib plus peg-interferon alpha induction and peg-interferon alpha maintenance therapy for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia patients; The tiger trial. Blood. 2023;142((Suppl. 1)):446. doi: 10.1182/blood-2023-182792. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saussele S., Richter J., Guilhot J., Gruber F.X., Hjorth-Hansen H., Almeida A., Janssen J.J.W.M., Mayer J., Koskenvesa P., Panayiotidis P., et al. Discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia (EURO-SKI): A prespecified interim analysis of a prospective, multicentre, non-randomised, trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:747–757. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30192-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

