Bedside Neuromodulation of Persistent Pain and Allodynia with Caloric Vestibular Stimulation
- PMID: 39457677
- PMCID: PMC11505407
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12102365
Bedside Neuromodulation of Persistent Pain and Allodynia with Caloric Vestibular Stimulation
Abstract
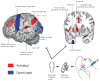
Background: Caloric vestibular stimulation (CVS) is a well-established neurological diagnostic technique that also induces many phenomenological modulations, including reductions in phantom limb pain (PLP), spinal cord injury pain (SCIP), and central post-stroke pain.
Objective: We aimed to assess in a variety of persistent pain (PP) conditions (i) short-term pain modulation by CVS relative to a forehead ice pack cold-arousal control procedure and (ii) the duration and repeatability of CVS modulations. The tolerability of CVS was also assessed and has been reported separately.
Methods: We conducted a convenience-based non-randomised single-blinded placebo-controlled study. Thirty-eight PP patients were assessed (PLP, n = 8; SCIP, n = 12; complex regional pain syndrome, CRPS, n = 14; non-specific PP, n = 4). Patients underwent 1-3 separate-day sessions of iced-water right-ear CVS. All but four also underwent the ice pack procedure. Analyses used patient-reported numerical rating scale pain intensity (NRS-PI) scores for pain and allodynia.
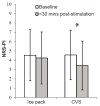
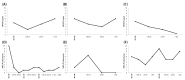
Results: Across all groups, NRS-PI for pain was significantly lower within 30 min post-CVS than post-ice pack (p < 0.01). Average reductions were 24.8% (CVS) and 6.4% (ice pack). CRPS appeared most responsive to CVS, while PLP and SCIP responses were less than expected from previous reports. The strongest CVS pain reductions lasted hours to over three weeks. CVS also induced substantial reductions in allodynia in three of nine allodynic CRPS patients, lasting 24 h to 1 month. As reported elsewhere, only one patient experienced emesis and CVS was widely rated by patients as a tolerable PP management intervention.
Conclusions: Although these results require interpretative caution, CVS was found to modulate pain relative to an ice pack control. CVS also modulated allodynia in some cases. CVS should be examined for pain management efficacy using randomised controlled trials.
Keywords: allodynia; caloric vestibular stimulation; complex regional pain syndrome; non-invasive brain stimulation; persistent pain; phantom limb pain; spinal cord injury pain; vestibular neuromodulation.
Conflict of interest statement
S.M.M. has received equipment for research from Soterix Medical Inc. P.B.F. has received equipment for research from MagVenture A/S, Medtronic Ltd., Neuronetics and Brainsway Ltd. and funding for research from Neuronetics. He is on scientific advisory boards for Bionomics Ltd. and LivaNova and is a founder of TMS Clinics Australia. S.M.M. and A.K.N. have received funding from Monash Institute of Medical Engineering to examine methods for CVS self-administration. If such methods are commercialised, Monash University, Monash Alfred Psychiatry Research Centre and authors S.M.M. and A.K.N. would receive royalties. The remaining authors have no competing interest related to this work to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Andersson G.B.J., Watkins-Castillo S.I. The Burden of Musculoskeletal Diseases in the United States. 3rd ed. United States Bone and Joint Initiative; Rosemont, IL, USA: 2014.
-
- Deloitte Access Economics . The Cost of Pain in Australia. Painaustralia; Deakin, Australia: 2019.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

