Effects of Perceptual-Cognitive Training on Anticipation and Decision-Making Skills in Team Sports: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39457791
- PMCID: PMC11505547
- DOI: 10.3390/bs14100919
Effects of Perceptual-Cognitive Training on Anticipation and Decision-Making Skills in Team Sports: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
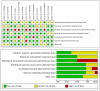
Team sports require athletes' exceptional perceptual-cognitive skills, such as anticipation and decision-making. Perceptual-cognitive training in laboratories aims to enhance these abilities. However, its effectiveness in real-game performance remains controversial, necessitating a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine optimal training methods. Following the PRISMA guidelines, we searched databases (e.g., PubMed, WOS, Scopus, and EBSCO) for relevant studies published before November 2023, assessed study quality, extracted important characteristics, and conducted a meta-analysis using Stata 15.1. This study was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023494324). A total of 22 quantitative studies involving 45 effect sizes were included. Perceptual-cognitive training positively influenced elite athletes' anticipation and decision-making. However, its transfer effect on real-game performance improvement (ES = 0.65) was inferior to laboratory performance improvement (ES = 1.51). Sub-group analyses indicated that the effects of training interventions varied based on stimulus presentation and intervention duration. Based on our findings, we concluded that while perceptual-cognitive training improved on-court performance, its transfer effects were limited. To maximize effectiveness, future interventions should use virtual reality to present training stimuli and incorporate participants' sport-specific responses to reflect real-game scenarios.
Keywords: decision-making and anticipation; meta-analysis; on-court transfer effect; optimal training methods; perceptual-cognitive training.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

