Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Immune and Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms in the Eriocheir japonica sinensis after Exposure to Ammonia
- PMID: 39457912
- PMCID: PMC11503868
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14202981
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Immune and Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms in the Eriocheir japonica sinensis after Exposure to Ammonia
Abstract
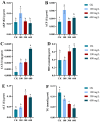
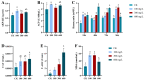
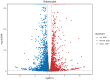
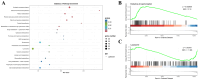
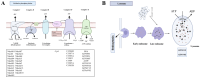
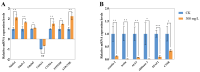
As a key species in freshwater aquaculture, Eriocheir japonica sinensis was subjected to ammonia stress to assess its impact on the hepatopancreas. A total of 4007 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified between control and treatment groups, comprising 1838 upregulated and 2169 downregulated genes. Following exposure to 300 mg/L of ammonia, the oxidative phosphorylation pathway was activated, while the lysosomal pathway was suppressed, thereby influencing immune functions. Thirteen DEGs from these pathways were further validated via qRT-PCR, revealing gene expression changes of one- to two-fold. Both acid phosphatase (ACP) and alkaline phosphatase (AKP) levels in the hepatopancreas and hemolymph initially increased and then decreased, indicating a disruption in immune functionality. Additionally, alanine transaminase (ALT) and triglyceride (TG) levels were measured, alongside catalase (CAT) activity, total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) content, all of which showed an upward trend, signifying oxidative stress and tissue damage. These results offer critical insights into the antioxidant and immune mechanisms of E. j. sinensis in ammonia-enriched environments.
Keywords: Eriocheir japonica sinensis; ammonia; gene expression; immune response; lysosomal pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Liu X.H. The biological characteristics and feeding technique of Eriocheir sinensis. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2009;48:158–160.
-
- Wang X., Yao Q., Zhang D.M., Lei X.Y., Wang S., Wan J.W., Guo Z.X. Effects of acute salinity stress on osmoregulation, antioxidant capacity and physiological metabolism of female Chinese mitten crabs (Eriocheir sinensis) Aquaculture. 2022;552:737989. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.737989. - DOI
-
- Sui L., Zhang F., Wang X., Bossier P., Sorgeloos P., Hänfling B. Genetic diversity and population structure of the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis in its native range. Mar. Biol. 2009;156:1573–1583. doi: 10.1007/s00227-009-1193-2. - DOI
-
- Chen D.W., Zhang M., Shrestha S. Compositional characteristics and nutritional quality of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) Food Chem. 2007;103:1343–1349. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.10.047. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

