Impact of a Bundle of Interventions on the Spectrum of Parenteral Drug Preparation Errors in a Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
- PMID: 39458002
- PMCID: PMC11509000
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13206053
Impact of a Bundle of Interventions on the Spectrum of Parenteral Drug Preparation Errors in a Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
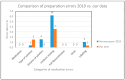
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the impact of a bundle of interventions on the error rates in preparing parenteral medications in a neonatal and pediatric intensive care unit (NICU/PICU). Methods: We conducted a prospective interventional study in a NICU/PICU in a tertiary university hospital as a follow-up to a prior study in the same setting. A clinical pharmacist and a pharmacy technician (PT) analyzed the workflow of drug preparation on the ward, identified high-alert medications, and defined a bundle of five interventions, which include the following: Drug Labeling: 1. EN ISO-DIVI labeling; Training: 2. Standardized preparation process on the ward; 3. eLearning Program; 4. Expert Consultations; and Location of Preparation: 5. Transfer of the preparation of high-alert medications and standardized preparations to the central pharmacy. After implementing the bundle of interventions, we observed the preparation process on the ward to evaluate if the implementation of the interventions had an impact on the quality of the drug preparation. Results: We observed 262 preparations in the NICU/PICU. Each single step of the preparation process was defined as an error opportunity. We defined seven error categories with an overall error opportunity of 1413. In total, we observed 11 errors (0.78%). The reduction in the overall error rate from 1.32% in the former study to 0.78% per preparation opportunity demonstrated that the implemented interventions were effective in enhancing medication safety. Conclusions: This study provides evidence that a bundle of interventions, including standardizing drug labeling, enhancing training, and centralizing the preparation of high-alert medications, can reduce medication errors in NICU/PICU settings.
Keywords: clinical pharmacist; drug preparation; error reduction; interventional study; medication errors; medication safety; neonatal intensive care; parenteral medications; pediatric intensive care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials