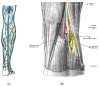
Morphological Variability of the Sural Nerve and Its Clinical Significance
- PMID: 39458004
- PMCID: PMC11508416
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13206055
Morphological Variability of the Sural Nerve and Its Clinical Significance
Abstract
The sural nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin on the distal posterolateral third of the lower extremity. The morphological variants are characterized by high variability. However, it most commonly arises from a union of the medial sural cutaneous nerve and the peroneal communicating branch of the common fibular nerve. This article overviews the anatomical and clinical significance of the sural nerve. Despite the remarkable development of genetic diagnostics, sural nerve biopsy is still a very important tool to diagnose peripheral neuropathies such as diabetic, vascular and inflammatory neuropathies. Furthermore, the sural nerve is also commonly transplanted due to its characteristics. Such a procedure is applicable in cases of segmental nerve loss, but it is also used to restore potency in patients after radical prostatectomy. The knowledge of anatomical variants of the sural nerve is also crucial as it allows to minimize its damage during surgical procedures. Furthermore, during an ankle surgery, a nerve block can be used to complement anesthesia. The major aim of this work is to review contributions of the sural nerve to physiological and pathophysiological processes.
Keywords: anatomical variations; peripheral neuropathy; sural biopsy; sural mononeuropathy; sural nerve; sural nerve entrapment; sural nerve graft.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anatomy of the sural nerve complex.J Hand Surg Am. 1987 Nov;12(6):1119-23. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(87)80129-6. J Hand Surg Am. 1987. PMID: 3693848
-
Compound nerve action potential of common peroneal nerve and sural nerve action potential in common peroneal neuropathy.J Korean Med Sci. 2008 Feb;23(1):117-21. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.117. J Korean Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 18303210 Free PMC article.
-
The bilateral anatomical variation of the sural nerve and a review of relevant literature.Anat Sci Int. 2014 Jan;89(1):57-61. doi: 10.1007/s12565-013-0195-9. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Anat Sci Int. 2014. PMID: 23917949 Review.
-
Sural nerve harvesting beyond the popliteal region allows a significant gain of donor nerve graft length.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008 Sep;122(3):798-805. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318180ed75. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008. PMID: 18766043
-
Sural nerve: imaging anatomy and pathology.Br J Radiol. 2023 Jan 1;96(1141):20220336. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220336. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36039944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anatomical Variations in the Formation of the Sural Nerve: A Pilot Study in a Sample of Lithuanian Cadavers.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Apr 5;61(4):671. doi: 10.3390/medicina61040671. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40282962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miniato M.A., Nedeff N. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb: Sural Nerve. - PubMed
-
- Teunissen L.L., Veldink J., Notermans N.C., Bleys R.L.A.W. Quantitative Assessment of the Innervation of Epineurial Arteries in the Peripheral Nerve by Immunofluorescence: Differences between Controls and Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2002;103:475–480. doi: 10.1007/s00401-001-0492-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources