It Takes Two to Make a Thing Go Right: Epistasis, Two-Component Response Systems, and Bacterial Adaptation
- PMID: 39458309
- PMCID: PMC11510482
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12102000
It Takes Two to Make a Thing Go Right: Epistasis, Two-Component Response Systems, and Bacterial Adaptation
Abstract
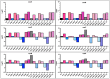
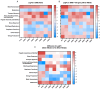
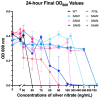
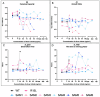
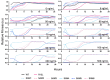
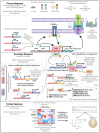
Understanding the interplay between genotype and fitness is a core question in evolutionary biology. Here, we address this challenge in the context of microbial adaptation to environmental stressors. This study explores the role of epistasis in bacterial adaptation by examining genetic and phenotypic changes in silver-adapted Escherichia coli populations, focusing on the role of beneficial mutations in two-component response systems (TCRS). To do this, we measured 24-hour growth assays and conducted whole-genome DNA and RNA sequencing on E. coli mutants that confer resistance to ionic silver. We showed recently that the R15L cusS mutation is central to silver resistance, primarily through upregulation of the cus efflux system. However, here we show that this mutation's effectiveness is significantly enhanced by epistatic interactions with additional mutations in regulatory genes such as ompR, rho, and fur. These interactions reconfigure global stress response networks, resulting in robust and varied resistance strategies across different populations. This study underscores the critical role of epistasis in bacterial adaptation, illustrating how interactions between multiple mutations and how genetic backgrounds shape the resistance phenotypes of E. coli populations. This work also allowed for refinement of our model describing the role TCRS genes play in bacterial adaptation by now emphasizing that adaptation to environmental stressors is a complex, context-dependent process, driven by the dynamic interplay between genetic and environmental factors. These findings have broader implications for understanding microbial evolution and developing strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance.
Keywords: bacterial adaptation; epistasis; gene-by-environment interactions; silver resistance; two-component response systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

