The Marine-Origin Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bacteria Micrococcus Antarcticus HZ Inhibits Pb Uptake in Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) and Affects Rhizosphere Microbial Communities
- PMID: 39458311
- PMCID: PMC11509687
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12102002
The Marine-Origin Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bacteria Micrococcus Antarcticus HZ Inhibits Pb Uptake in Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) and Affects Rhizosphere Microbial Communities
Abstract
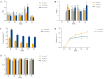
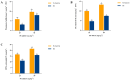
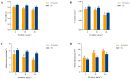
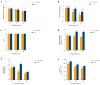
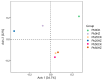
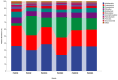
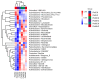
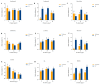
Exopolysaccharides (EPSs) produced by microorganisms play an important role in biotolerance and reducing heavy metal (HM) contamination by limiting the migration of HMs into plants. However, research on the application of EPS-producing marine bacteria for soil heavy metal remediation remains limited, particularly regarding their mechanisms of HM immobilization in soil and impact on plant growth. In this study, the EPS-producing marine bacterium Micrococcus antarcticus HZ was investigated for its ability to immobilize Pb and produce EPSs in soil filtrate. The effects on the growth quality and biomass of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.), as well as bacterial communities in inter-root soil contaminated with Pb, were also investigated. The results indicated that HZ could reduce the Pb concentration in the soil filtrate, achieving a removal rate of 43.25-63.5%. The EPS content and pH levels increased in the presence of Pb. Pot experiments showed that adding HZ significantly increased the biomass of pakchoi (9.45-14.69%), vitamin C (Vc) (9.69-12.92%), and soluble protein content (22.58-49.7%). HZ reduced the Pb content in the roots (17.52-47.48%) and leaves (edible tissues) (43.82-52.83%) of pakchoi. HZ increased soil enzyme activities (alkaline phosphatase, dehydrogenase, and urease), and the contents of ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen. Additionally, HZ also increased the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria (e.g., Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Chlorobacteria) in the inter-root soil, which have prophylactic and heavy-metal fixation functions. In summary, HZ reduces effective Pb content in edible tissues, roots, and inter-root soil by regulating inter-root soil microbial community structure, increasing soil pH, nitrogen content, and soil enzyme activity, and altering dominant phylum abundance.
Keywords: Pb-immobilizing; bacterial community; bioremediation; exopolysaccharides (EPSs); heavy-metal-contaminated soil; marine bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria enhanced Pb immobilization and influenced the microbiome composition in rhizosphere soil of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.).Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1117312. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1117312. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36970682 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy metal-immobilizing bacteria increase the biomass and reduce the Cd and Pb uptake by pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) in heavy metal-contaminated soil.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020 Jun 1;195:110375. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110375. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020. PMID: 32200142
-
Biochar's role in improving pakchoi quality and microbial community structure in rhizosphere soil.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 18;12:e16733. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16733. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38515457 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of Combined Application of Different Nitrogen Fertilizers and Biochar on Cadmium Uptake by Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) in Cadmium Contaminated Soil].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2023 Aug 8;44(8):4489-4496. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202209248. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2023. PMID: 37694643 Chinese.
-
Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bacteria Regulate Soil Aggregates and Bacterial Communities to Inhibit the Uptake of Cadmium and Lead by Lettuce.Microorganisms. 2024 Oct 22;12(11):2112. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12112112. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39597502 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- ZR2022MD097/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- 2020KJC-ZD08/Science, Education and Industry Integration Innovation Pilot Project of Qilu Univer sity of Technology
- 2024ZDZX03/Science, Education and Industry Integration Innovation Pilot Project of Qilu Univer sity of Technology
- 2022JBZ01-06/Major Innovation Project of Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

