Association between Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Fish Phenotype and the Post-Larval Bacteriome
- PMID: 39458323
- PMCID: PMC11510086
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12102014
Association between Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Fish Phenotype and the Post-Larval Bacteriome
Abstract
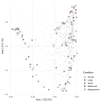
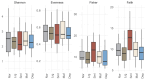
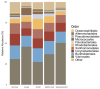
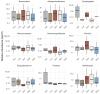
Over the past decade, an increasing number of studies have emphasized the importance of the host microbiome in influencing organismal health and development. Aligned with this understanding, our study aimed to investigate the potential association between the turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) phenotypic traits and the post-larval bacteriome. Turbot post-larvae were sampled from twenty randomly selected production cycles thirty days after hatching (DAH) across multiple post-larval production batches over a three-month period (April to June). Fish were selectively sampled based on five phenotypic traits, namely, normal, large, small, malformed, and depigmented. Our results showed that small-sized post-larvae had significantly higher bacterial phylogenetic diversity in their bacterial communities than all other phenotypes. A more in-depth compositional analysis also revealed specific associations between certain bacterial taxa and fish phenotypes. For example, the genera Aliivibrio and Sulfitobacter were enriched in small-sized post-larvae, while the family Micrococcaceae were predominantly found in larger post-larvae. Furthermore, genus Exiguobacterium was linked to depigmented larvae, and genus Pantoea was more prevalent in normal post-larvae. These observations underscore the importance of further research to understand the roles of these bacterial taxa in larval growth and phenotypic differentiation. Such insights could contribute to developing microbiome modulation strategies, which may enhance turbot post-larval health and quality and improve larviculture production.
Keywords: Cytophagales flatfish; larviculture; malpigmentation; microbiome; skeletal abnormalities.
Conflict of interest statement
The company was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing the Effects of Rotifer Feed Enrichments on Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae and Post-Larvae Gut-Associated Bacterial Communities.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 17;11(2):520. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020520. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838485 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Vibrio scophthalmi and its phenotypic diversity in turbot larvae.Environ Microbiol. 2004 Mar;6(3):209-17. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2004.00555.x. Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14871205
-
Vibrio splendidus biotype 1 as a cause of mortalities in hatchery-reared larval turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.).J Appl Microbiol. 2005;99(2):243-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02602.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16033454
-
Roles of insulin-like growth factors in metamorphic development of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus).Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018 Sep 1;265:61-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.01.030. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29409593 Review.
-
Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) vs. VHSV (Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus): A Review.Front Physiol. 2016 May 26;7:192. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00192. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27303308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reitan K.I., Rainuzzo J.R., Olsen Y. Influence of Lipid Composition of Live Feed on Growth, Survival and Pigmentation of Turbot Larvae. Aquac. Int. 1994;2:33–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00118531. - DOI
-
- Denson M.R., Smith T.I.J. Diet and Light Intensity Effects on Survival, Growth and Pigmentation of Southern Flounder Paralichthys lethostigma. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1997;28:366–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-7345.1997.tb00283.x. - DOI
-
- Estevez A., McEvoy L.A., Bell J.G., Sargent J.R. Growth, Survival, Lipid Composition and Pigmentation of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae Fed Live-Prey Enriched in Arachidonic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids. Aquaculture. 1999;180:321–343. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00209-4. - DOI
-
- Eissa A.E., Abu-Seida A.M., Ismail M.M., Abu-Elala N.M., Abdelsalam M. A Comprehensive Overview of the Most Common Skeletal Deformities in Fish. Aquac. Res. 2021;52:2391–2402. doi: 10.1111/are.15125. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

