Oral Administration of a Novel, Synthetic Ketogenic Compound Elevates Blood β-Hydroxybutyrate Levels in Mice in Both Fasted and Fed Conditions
- PMID: 39458521
- PMCID: PMC11510390
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16203526
Oral Administration of a Novel, Synthetic Ketogenic Compound Elevates Blood β-Hydroxybutyrate Levels in Mice in Both Fasted and Fed Conditions
Abstract
Background/objectives: Elevating ketone levels with therapeutic nutritional ketosis can help to metabolically manage disease processes associated with epilepsy, diabetes, obesity, cancer, and neurodegenerative disease. Nutritional ketosis can be achieved with various dieting strategies such as the classical ketogenic diet, the modified Atkins diet, caloric restriction, periodic fasting, or the consumption of exogenous ketogenic supplements such as medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). However, these various strategies can be unpleasant and difficult to follow, so that achieving and sustaining nutritional ketosis can be a major challenge. Thus, investigators continue to explore the science and applications of exogenous ketone supplementation as a means to further augment the therapeutic efficacy of this metabolic therapy.
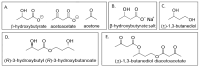
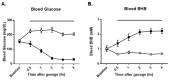
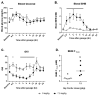
Methods: Here, we describe a structurally new synthetic triglyceride, glycerol tri-acetoacetate (Gly-3AcAc), that we prepared from glycerol and an acetoacetate precursor that produces hyperketonemia in the therapeutic range (2-3 mM) when administered to mice under both fasting and non-fasting conditions. Animal studies were undertaken to evaluate the potential effects of eliciting a ketogenic response systemically. Acute effects (24 h or less) were determined in male VM/Dk mice in both fasted and unfasted dietary states.
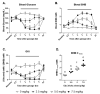
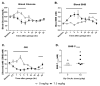
Results: Concentration levels of β-hydroxybutyrate in blood were elevated (βHB; 2-3 mM) under both conditions. Levels of glucose were reduced only in the fasted state. No detrimental side effects were observed.
Conclusions: Pending further study, this novel compound could potentially add to the repertoire of methods for inducing therapeutic nutritional ketosis.
Keywords: diabetes; exogenous ketones; hyperketonemia; hypoglycemia; ketogenic diet; ketone metabolic therapy; ketosis; medium-chain triglycerides; nutritional supplements.
Conflict of interest statement
D.P.D. is an inventor on a patent entitled “Composition and Methods of Elevating and Sustaining Ketosis” USPTO#20170266148. D.P.D. is an owner of Ketone Technologies LLC, is a paid advisor to Nutrish Brands, and has received honoraria for speaking at symposia. All the other authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
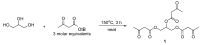

Similar articles
-
Nutritional ketosis delays the onset of isoflurane induced anesthesia.BMC Anesthesiol. 2018 Jul 18;18(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0554-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 30021521 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous Ketone Supplements Improved Motor Performance in Preclinical Rodent Models.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 15;12(8):2459. doi: 10.3390/nu12082459. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32824223 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exogenous ketone supplementation on blood ketone, glucose, triglyceride, and lipoprotein levels in Sprague-Dawley rats.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016 Feb 4;13:9. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0069-y. eCollection 2016. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26855664 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of G protein-coupled receptors by ketone bodies: Clinical implication of the ketogenic diet in metabolic disorders.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 20;13:972890. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.972890. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36339405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of Exogenous Ketogenic Supplements on Aging Processes and Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 26;13(7):2197. doi: 10.3390/nu13072197. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34206738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Masood W., Annamaraju P., Khan Suheb M.Z., Uppaluri K.R. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Ketogenic Diet. - PubMed
-
- Waldman H.S., O’Neal E.K., Barker G.A., Witt C.R., Lara D.A., Huber A.K., Forsythe V.N., Koutnik A.P., D’Agostino D.P., Staiano W., et al. A Ketone Monoester with Carbohydrate Improves Cognitive Measures Postexercise, but Not Performance in Trained Females. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2024;56:725–736. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000003352. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

