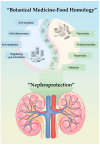
Renal Health Through Medicine-Food Homology: A Comprehensive Review of Botanical Micronutrients and Their Mechanisms
- PMID: 39458524
- PMCID: PMC11510533
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16203530
Renal Health Through Medicine-Food Homology: A Comprehensive Review of Botanical Micronutrients and Their Mechanisms
Abstract
Background: As an ancient concept and practice, "food as medicine" or "medicine-food homology" is receiving more and more attention these days. It is a tradition in many regions to intake medicinal herbal food for potential health benefits to various organs and systems including the kidney. Kidney diseases usually lack targeted therapy and face irreversible loss of function, leading to dialysis dependence. As the most important organ for endogenous metabolite and exogenous nutrient excretion, the status of the kidney could be closely related to daily diet. Therefore, medicinal herbal food rich in antioxidative, anti-inflammation micronutrients are ideal supplements for kidney protection. Recent studies have also discovered its impact on the "gut-kidney" axis.
Methods: Here, we review and highlight the kidney-protective effects of botanicals with medicine-food homology including the most frequently used Astragalus membranaceus and Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, concerning their micronutrients and mechanism, offering a basis and perspective for utilizing and exploring the key substances in medicinal herbal food to protect the kidney.
Results: The index for medicine-food homology in China contains mostly botanicals while many of them are also consumed by people in other regions. Micronutrients including flavonoids, polysaccharides and others present powerful activities towards renal diseases.
Conclusions: Botanicals with medicine-food homology are widely speeded over multiple regions and incorporating these natural compounds into dietary habits or as supplements shows promising future for renal health.
Keywords: botanicals; gut–kidney axis; kidney protection; medicine–food homology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Medicinal plants and their preparations in the European market: Why has the harmonization failed? The cases of St. John's wort, valerian, ginkgo, ginseng, and green tea.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jan;81:153421. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153421. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33291029 Review.
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
Polygonati Rhizoma with the homology of medicine and food: A review of ethnopharmacology, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and applications.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jun 12;309:116296. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116296. Epub 2023 Feb 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36841378 Review.
-
Health benefits of herbs and spices: the past, the present, the future.Med J Aust. 2006 Aug 21;185(S4):S1-S24. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2006.tb00548.x. Med J Aust. 2006. PMID: 17022438 Review.
-
Protection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in kidney epithelium by Angelica and Astragalus.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:412-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.027. Epub 2015 Dec 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26719285
References
-
- Mody H., Ramakrishnan V., Chaar M., Lezeau J., Rump A., Taha K., Lesko L., Ait-Oudhia S. A Review on Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity: Pathophysiological Mechanisms, Drug Classes, Clinical Management, and Recent Advances in Mathematical Modeling and Simulation Approaches. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020;9:896–909. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.879. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gaitonde D.Y., Cook D.L., Rivera I.M. Chronic Kidney Disease: Detection and Evaluation. Am. Fam. Physician. 2017;96:776–783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82173888/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81973290/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021-I2M-1-007/Medical and Health Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
- 2022-I2M-2-002/Medical and Health Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-028/Medical and Health Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials