Vitamin D Supply of Twins during Fetal Life, Its Relation to Anthropometric Parameters of Newborns and the Analysis of Other Factors Related to Birth Size
- PMID: 39458529
- PMCID: PMC11510133
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16203535
Vitamin D Supply of Twins during Fetal Life, Its Relation to Anthropometric Parameters of Newborns and the Analysis of Other Factors Related to Birth Size
Abstract
Background/objectives: Vitamin D deficiencies are very common in pregnant women, raising concerns about adverse health outcomes in children. This issue has hardly been studied in multiple pregnancies, the prevalence of which has been steadily increasing. Therefore, our study investigated the relationship between newborns' anthropometric parameters and the concentration of 25(OH)D in maternal blood of women with twin pregnancies and umbilical cord blood.
Methods: The study included 50 women who gave birth after the 36th week of twin gestation. The concentration of 25(OH)D was determined in maternal blood collected during the antenatal period and in the umbilical cord blood of 100 newborns. Anthropometric parameters of the newborns (birth weight, length and head and chest circumference) were obtained from hospital records. Data on nutrition and lifestyle during pregnancy were collected from the patients during an interview conducted by a dietitian.
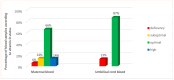
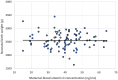
Results: No relationship between maternal and neonatal cord blood vitamin D concentrations and any of the anthropometric parameters of the newborns was found. However, only 6% of the mothers and 13% of the newborns had vitamin D deficiency (≤20 ng/mL). The type of pregnancy and maternal height were the main factors associated with neonatal size. Newborns from dichorionic pregnancies were on average 202 g heavier (p < 0.001) and 1 cm longer (p = 0.006) than newborns from monochorionic pregnancies. Newborns of mothers ≤160 cm in height had on average 206 g lower birth weight (p = 0.006) and were 3.5 cm shorter (p = 0.003) compared to newborns of taller mothers.
Conclusions: Therefore, in our study, the neonatal size of twins was not related to the vitamin D status but to other factors such as the type of pregnancy and maternal height.
Keywords: neonatal parameters; twin pregnancy; umbilical cord blood; vitamin D concentration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- van der Pligt P.F., Ellery S.J., de Guingand D.L., Abbott G., Della Gatta P.A., Daly R.M. Maternal plasma vitamin D levels across pregnancy are not associated with neonatal birthweight: Findings from an Australian cohort study of low-risk pregnant women. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023;23:67. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-05336-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gallo S., McDermid J.M., Al-Nimr R.I., Hakeem R., Moreschi J.M., Pari-Keener M., Stahnke B., Papoutsakis C., Handu D., Cheng F.W. Vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy: An evidence analysis center systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020;120:898–924.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2019.07.002. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical