Respiratory Delivery of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG by Vibrating-Mesh and Jet Nebulisation
- PMID: 39458655
- PMCID: PMC11510752
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101326
Respiratory Delivery of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG by Vibrating-Mesh and Jet Nebulisation
Abstract
Background: The use of probiotic bacteria to improve lung health has been gaining interest. Although the oral delivery of probiotics and their effects are well documented, there is currently limited knowledge on the respiratory delivery of probiotics.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate whether nebulisation is suitable for delivering Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) into the lungs for the potential treatment of bacterial pulmonary infections.
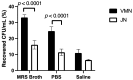
Methods: It compared the dose output and aerosol performance of a vibrating-mesh nebuliser (VMN) and a jet nebuliser (JN) in nebulising LGG suspended in de Man Rogosa Sharpe (MRS) broth, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), or normal saline (0.9% w/v sodium chloride in water).
Results: The VMN consistently produced a higher output than the JN for all liquid media, indicating that VMN was more efficient. The fine-particle fractions of both nebulisers were comparable for a given medium. The highest fine-particle fraction was achieved with LGG suspended in MRS broth for both nebulisers (20.5 ± 2.8% for VMN; 18.7 ± 3.4% for JN). This suggests that the aerosol performance of nebulised probiotics may depend on the medium in which the probiotic bacteria were suspended.
Conclusions: Therefore, this study demonstrated that the nebulisation efficiency of LGG depended on the nebuliser type and liquid medium of the probiotic suspension.
Keywords: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG; aerosol; bacteria; droplet; inhalation; jet nebuliser; nebulisation; probiotics; vibrating-mesh nebuliser.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Probiotics™ Australia unconditionally donated the probiotic bacteria for the experiments. This company has no role or interest in the work. The authors have no relationship with Probiotics™ Australia.
Figures










References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 5 November 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

