NMDA Receptors: Distribution, Role, and Insights into Neuropsychiatric Disorders
- PMID: 39458906
- PMCID: PMC11509972
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17101265
NMDA Receptors: Distribution, Role, and Insights into Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Abstract
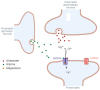
Background: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are members of the ionotropic glutamate receptor family. These ligand-gated channels are entwined with numerous fundamental neurological functions within the central nervous system (CNS), and numerous neuropsychiatric disorders may arise from their malfunction.
Methods: The purpose of the present review is to provide a detailed description of NMDARs by addressing their molecular structures, activation mechanisms, and physiological roles in the mammalian brain. In the second part, their role in various neuropsychiatric disorders including stroke, epilepsy, anti-NMDA encephalitis, Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases, schizophrenia, depression, neuropathic pain, opioid-induced tolerance, and hyperalgesia will be covered.
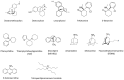
Results: Finally, through a careful exploration of the main non-competitive NMDARs antagonists (channel-blockers).
Conclusion: We discuss the strengths and limitations of the various molecular structures developed for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: NMDA channel blockers; NMDA receptors; neuropsychiatric disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fujitani S., Matsuda K., Nakamura F., Baba K., Usui N., Tottori T., Mihara T., Terada K., Usui K., Inoue Y., et al. Statistical parametric mapping of interictal 123I-iomazenil SPECT in temporal lobe epilepsy surgery. Epilepsy Res. 2013;106:173–180. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.03.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

