Multifaceted Heparin: Diverse Applications beyond Anticoagulant Therapy
- PMID: 39459002
- PMCID: PMC11510354
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17101362
Multifaceted Heparin: Diverse Applications beyond Anticoagulant Therapy
Abstract
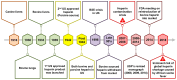
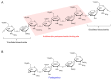
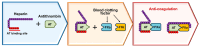
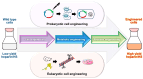
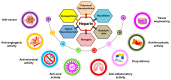
Heparin, a naturally occurring polysaccharide, has fascinated researchers and clinicians for nearly a century due to its versatile biological properties and has been used for various therapeutic purposes. Discovered in the early 20th century, heparin has been a key therapeutic anticoagulant ever since, and its use is now implemented as a life-saving pharmacological intervention in the management of thrombotic disorders and beyond. In addition to its known anticoagulant properties, heparin has been found to exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and anti-tumorigenic activities, which may lead to its widespread use in the future as an essential drug against infectious diseases such as COVID-19 and in various medical treatments. Furthermore, recent advancements in nanotechnology, including nano-drug delivery systems and nanomaterials, have significantly enhanced the intrinsic biofunctionalities of heparin. These breakthroughs have paved the way for innovative applications in medicine and therapy, expanding the potential of heparin research. Therefore, this review aims to provide a creation profile of heparin, space for its utilities in therapeutic complications, and future characteristics such as bioengineering and nanotechnology. It also discusses the challenges and opportunities in realizing the full potential of heparin to improve patient outcomes and elevate therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: anticoagulant; bioengineering; glycosaminoglycan; heparin; nano-drug delivery systems; nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioengineered heparin: Advances in production technology.Biotechnol Adv. 2024 Dec;77:108456. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2024.108456. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Biotechnol Adv. 2024. PMID: 39326809 Review.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Pharmacological and clinical application of heparin progress: An essential drug for modern medicine.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jul;139:111561. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111561. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33848775 Review.
-
Heparin: An old drug for new clinical applications.Carbohydr Polym. 2022 Nov 1;295:119818. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119818. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Carbohydr Polym. 2022. PMID: 35989029 Review.
-
Heparin: new life for an old drug.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017 Jul;12(14):1727-1744. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0127. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28635544 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Biomarkers in Thrombophilia-Related Pregnancy Complications: Mechanisms, Diagnostic Potential, and Therapeutic Implications: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 20;25(24):13634. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413634. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

