High-CBD Extract (CBD-X) in Asthma Management: Reducing Th2-Driven Cytokine Secretion and Neutrophil/Eosinophil Activity
- PMID: 39459021
- PMCID: PMC11510504
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17101382
High-CBD Extract (CBD-X) in Asthma Management: Reducing Th2-Driven Cytokine Secretion and Neutrophil/Eosinophil Activity
Abstract
Background/objectives: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways affecting over 10% of the global population. It is characterized by airway inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness, driven predominantly by type 2 helper T cells (Th2) and type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) in a subset of patients. However, a significant portion of asthmatic individuals present with "type 2-low" asthma that is often refractory to standard inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) therapy. Therefore, developing innovative therapeutic strategies has become essential. Recent studies have highlighted cannabidiol (CBD) as a promising anti-inflammatory agent capable of modulating immune responses. This study investigates the therapeutic potential of a high-CBD extract (CBD-X) in asthma.
Methods: We evaluated the effects of CBD-X on cells involved in asthma pathogenesis using primary human Th2 cells, neutrophils, and asthma mouse model.
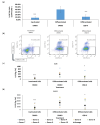
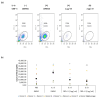
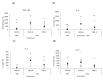
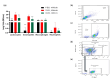
Results: Our findings indicate that CBD-X extract inhibits Th2 differentiation and reduces the secretion of IL-5 and IL-13, which are crucial cytokines in asthma. Additionally, CBD-X significantly reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-8 and IL-6 in neutrophils and impairs their migration, a critical step in airway inflammation. In a murine asthma model, CBD-X administration led to marked downregulation of IgE and pro-asthmatic cytokines, along with reduced leukocyte, eosinophil, and neutrophil infiltration in lung tissues.
Conclusions: These results suggest that CBD-X extract could offer a novel and complementary approach to managing both type 2-high and type 2-low asthma by targeting key inflammatory pathways and modulating immune cell behavior.
Keywords: CBD extracts; IgE; OVA-induced asthmatic mouse model; asthma; cytokines; eosinophil; migration; neutrophil; type 2 helper T cells (Th2).
Conflict of interest statement
This study received funding from Raphael Pharmaceutical Inc. The funders were not involved in any aspect of the study. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wu W., Bang S., Bleecker E.R., Castro M., Denlinger L., Erzurum S.C., Fahy J.V., Fitzpatrick A.M., Gaston B.M., Hastie A.T., et al. Multiview Cluster Analysis Identifies Variable Corticosteroid Response Phenotypes in Severe Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019;199:1358–1367. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201808-1543OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

