Hydrogel Containing Propolis: Physical Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Activities for Potential Use in the Treatment of Skin Lesions
- PMID: 39459039
- PMCID: PMC11510207
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17101400
Hydrogel Containing Propolis: Physical Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Activities for Potential Use in the Treatment of Skin Lesions
Abstract
Background: Skin injury affects the integrity of the skin structure and induces the wound healing process, which is defined by a well-coordinated series of cellular and molecular reactions that aim to recover or replace the injured tissue. Hydrogels are a group of promising biomaterials that are able to incorporate active ingredients for use as dressings. This study aimed to synthesize hydrogels with and without propolis extract and evaluate their physical characteristics and biological activities in vitro for potential use as active dressings in the treatment of skin lesions.
Methods: The antifungal [Candida albicans (C. albicans) and Candida tropicalis (C. tropicalis)] and antibacterial [Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Pseudomonas aeruginosas (P. aeruginosas) and Escherichia coli (E. coli)] activity was assessed by the microdilution method in plates and antioxidant potential by the reduction of the phosphomolybdate complex.
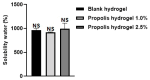
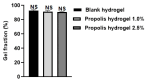
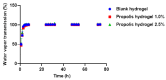
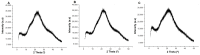
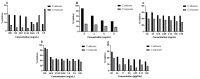
Results: The hydrogels showed good water absorption capacity, high solubility, and high gel fraction, as well as good porosity, water retention, and vapor transmission rates. They revealed a totally amorphous structure. The extract and the hydrogels containing the propolis extract (1.0% and 2.5%) did not inhibit fungal growth. However, they showed antibacterial activity against strains of S. aureus and P. aeruginosas. Regarding the E. coli strain, only the extract inhibited its growth. It showed good antioxidant activity by the evaluation method used.
Conclusions: Therefore, the hydrogels containing propolis extract can be a promising alternative with antibacterial and antioxidant action for use as dressings for the treatment of skin lesions.
Keywords: antimicrobial; antioxidant; biomaterial; chronic wounds; natural product.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








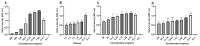

References
-
- Permyakova E.S., Solovieva A.O., Sitnikova N., Kiryukhantsev-Korneev P.V., Kutzhanov M.K., Sheveyko A.N., Ignatov S.G., Slukin P.V., Shtansky D.V., Manakhov A.M. Polycaprolactone nanofibers functionalized by fibronectin/gentamicin and implanted silver for enhanced antibacterial properties, cell adhesion, and proliferation. Polymers. 2024;16:261. doi: 10.3390/polym16020261. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Quiñones-Vico M.I., Fernández-González A., Ubago-Rodríguez A., Moll K., Norrby-Teglund A., Svensson M., Gutiérrez-Fernández J., Torres J.M., Arias-Santiago S. Antibiotics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa on human skin cell lines: Determination of the highest non-cytotoxic concentrations with antibiofilm capacity for wound healing strategies. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16:117. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

