New Role of the Serotonin as a Biomarker of Gut-Brain Interaction
- PMID: 39459580
- PMCID: PMC11509611
- DOI: 10.3390/life14101280
New Role of the Serotonin as a Biomarker of Gut-Brain Interaction
Abstract
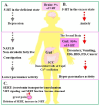
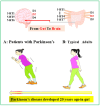
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine: 5-HT), a neurotransmitter that regulates mood in the brain and signaling in the gut, has receptors throughout the body that serve various functions, especially in the gut and brain. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are used to treat depression, but their efficacy is uncertain. Depression is often associated with early gastrointestinal symptoms. Gut disorders such as functional dyspepsia (FD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD), are linked to elevated serotonin levels. In this review, we would like to discuss the approach of using serotonin as a biomarker for gut-brain, and body-wide organ communication may lead to the development of preventive and innovative treatments for gut-brain disorders, offering improved visibility and therapeutic monitoring. It could also be used to gauge stress intensity for self-care and mental health improvement.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; functional dyspepsia (FD); gut homeostasis; gut–brain interaction; inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); mood; serotonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hatamnejad M.R., Ghavami S.B., Shirvani M., Ahmadabad M.A., Shahrokh S., Farmani M., Sherkat G., Aghdaei H.A., Zali M.R. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and inflammatory bowel disease; Beneficial or malpractice. Front. Immunol. 2022;13:980189. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.980189. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

