Recycled Aggregates Influence on the Mechanical Properties of Cement Lime-Based Mortars
- PMID: 39459826
- PMCID: PMC11509867
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17205122
Recycled Aggregates Influence on the Mechanical Properties of Cement Lime-Based Mortars
Abstract
The current framework for managing construction waste, guided by European Union regulations, calls for an integrated waste management system. However, the reuse of old plaster waste, particularly from deteriorated facades, remains underexplored. This study investigates the potential of repurposing old plaster waste as a substitute for aggregates and cement in mortars, with the aim of promoting environmental sustainability and resource efficiency. Three mortar mixes were analyzed: a control mix, a mix with 45% waste replacing aggregates, and a mix with 10% waste replacing cement. Results show that replacing 45% of aggregates with plaster waste led to a 30% reduction in flexural strength, while the 10% cement replacement increased flexural strength by 6%. Compressive strength dropped by 27% and 38% for cement and aggregate replacements, respectively. Despite these reductions, the waste replacement remained within acceptable limits for structural integrity. Further microscopic analysis revealed that the incomplete integration of portlandite particles from the waste contributed to non-uniform bonding and crystal formation, weakening the mortar's structure. This research demonstrates the feasibility of reusing old plaster waste, offering a novel approach to reducing construction waste and promoting a circular economy. It contributes to filling the knowledge gap on the reuse of plaster mortars while aligning with sustainable construction goals.
Keywords: construction waste; fractography; mineralogical investigation; plastering mortars; sustainable development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
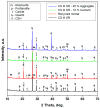
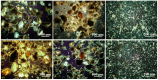
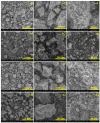
References
-
- Reducing the Impact of Construction on the Environment—ISO Press Release no. 1344/2010. [(accessed on 11 August 2022)]. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sustainable_development.
-
- Hiete M. Handbook of Recycled Concrete and Demolition Waste. Woodhead Publishing; Sawston, MA, USA: 2013. Waste management plants and technology for recycling construction and demolition (C&D) waste: State-of-the-art and future challenges; pp. 53–75. (Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering).
-
- Saitis C., Manea L.D., Plesa L.M., Saitis L.R. Recycling Plaster Waste as a Substitute for Aggregates in Obtaining Plastering Mortars. Buildings. 2023;13:491. doi: 10.3390/buildings13020491. - DOI
-
- Catarina N., Jorge B., Rosario V. Using Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregate for Mortar Production. Mater. Res. 2014;17:168–177.
-
- Nedeljković M., Visser J., Šavija B., Valcke S., Schlangen E. Use of fine recycled concrete aggregates in concrete: A critical review. J. Build. Eng. 2021;38:102196. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102196. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

