Enhanced Transcription of Human Endogenous Retroviruses and TRIM28 Downregulation in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 39459904
- PMCID: PMC11512322
- DOI: 10.3390/v16101570
Enhanced Transcription of Human Endogenous Retroviruses and TRIM28 Downregulation in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
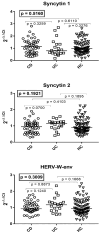
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes patients affected by Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. IBD is thought to be a chronic immune-mediated disease, but its origin remains elusive, and this limits new therapeutic approaches. Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) originate from ancestral infections and represent 8% of the human genome. HERVs are no longer infectious, but some retroviral sequences can be activated, and their aberrant expressions have been implicated in inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. HERV transcription is regulated by TRIM28 and SETDB1, which are also directly involved in epigenetic processes and modulation of the immune response. Using a PCR real-time Taqman amplification assay, we assessed, for the first time, the transcription levels of pol genes of HERV-H, -K, and -W families of env genes of syncytin 1 (SYN1), SYN2, and HERV-W, as well as of TRIM28 and SETDB1 in the whole blood of 48 patients with Crohn's disease (CD), 20 with ulcerative colitis (UC), and in healthy controls (HC) of comparable age. The transcriptional levels of HERV-H-pol (p = 0.0003) and HERV-K-pol (p = 0.001) were significantly higher in IBD patients compared with HC, with no differences between patients with CD and UC. No significant differences were found for the remaining HERVs between IBD patients and HC. The transcript levels of TRIM28 were significantly downregulated in IBD patients (p < 0.001), without differences between CD and UC, while the SETDB1 levels were preserved. The enhanced transcription of HERV-H-pol and HERV-K-pol, as well as the impaired activation of TRIM28, were not influenced by clinical disease activity and type of treatment. The overexpression of HERVs and impaired transcription of TRIM28 in patients affected by CD or UC suggest that they might be the main actors in the pathophysiology of IBD, opening the way to innovative targeted interventions.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; IBD; SETDB1; TRIM28; human endogenous retroviruses; pathogenesis; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kalla R., Adams A.T., Nowak J.K., Bergemalm D., Vatn S., Ventham N.T., Kennedy N.A., Ricanek P., Lindstrom J., IBD-Character Consortium et al. Analysis of Systemic Epigenetic Alterations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Defining Geographical, Genetic and Immune-Inflammatory Influences on the Circulating Methylome. J. Crohns Colitis. 2023;17:170–184. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stankey C.T., Bourges C., Haag L.M., Turner-Stokes T., Piedade A.P., Palmer-Jones C., Papa I., Silva Dos Santos M., Zhang Q., Cameron A.J., et al. A Disease-Associated Gene Desert Directs Macrophage Inflammation through ETS2. Nature. 2024;630:447–456. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07501-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

