Diagnostic Value of Anti-HTLV-1-Antibody Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy
- PMID: 39459915
- PMCID: PMC11512244
- DOI: 10.3390/v16101581
Diagnostic Value of Anti-HTLV-1-Antibody Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy
Abstract
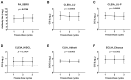
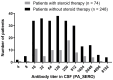
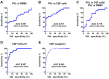
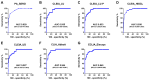
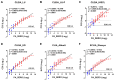
The diagnostic accuracy of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) anti-human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1) antibody testing for HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM) remains unclear. Therefore, we measured the anti-HTLV-1 antibody levels in CSF using various test kits, evaluated the stability of CSF antibodies, and performed a correlation analysis using the particle agglutination (PA) method, as well as a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis between patients with HAM and carriers. The CSF anti-HTLV-1 antibody levels were influenced by freeze-thaw cycles but remained stable when the CSF was refrigerated at 4 °C for up to 48 h. Measurements from 92 patients (69 patients with HAM and 23 carriers) demonstrated a strong correlation (r > 0.9) with the PA method across all six quantifiable test kits. All six test kits, along with CSF neopterin and CXCL10, exhibited areas under the ROC curve greater than 0.9, indicating a high diagnostic performance for HAM. Among these, five test kits, Lumipulse and Lumipulse Presto HTLV-I/II, HISCL-UD (a kit under development), HTLV-Abbott, and Elecsys HTLV-I/II, established a cutoff with 100% sensitivity and maximum specificity, achieving a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity ranging from 43.5% to 56.5%. This cutoff value, in combination with clinical findings, will aid in the accurate diagnosis of HAM.
Keywords: HTLV-1-associated myelopathy; anti-HTLV-1 antibody; cerebrospinal fluid; diagnosis; human T-cell leukemia virus type 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Poiesz B.J., Ruscetti F.W., Gazdar A.F., Bunn P.A., Minna J.D., Gallo R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1980;77:7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hinuma Y., Nagata K., Hanaoka M., Nakai M., Matsumoto T., Kinoshita K.I., Shirakawa S., Miyoshi I. Adult T-cell leukemia: Antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1981;78:6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6476. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 22FC1013/Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant on Rare and Intractable Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan
- JP22fk0108124, JP23ek0109529, and JP24ek0109735/Practical Research Project for Rare/Intractable Diseases of the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

