Tracking the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease after Almond and Oat Milk Intervene or Statin Medication with a Powerful Reflex SH-SAW POCT Platform
- PMID: 39459999
- PMCID: PMC11511040
- DOI: 10.3390/s24206517
Tracking the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease after Almond and Oat Milk Intervene or Statin Medication with a Powerful Reflex SH-SAW POCT Platform
Abstract
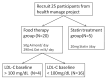
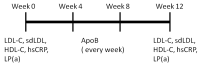
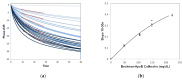
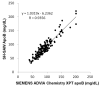
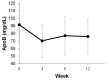
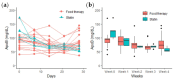
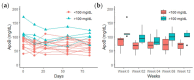
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) represents the leading cause of death worldwide. For individuals at elevated risk for cardiovascular disease, early detection and monitoring of lipid status is imperative. The majority of lipid measurements conducted in hospital settings employ optical detection, which necessitates the use of relatively large-sized detection machines. It is, therefore, necessary to develop point-of-care testing (POCT) for lipoprotein in order to monitor CVD. To enhance the management and surveillance of CVD, this study sought to develop a POCT approach for apolipoprotein B (ApoB) utilizing a shear horizontal surface acoustic wave (SH-SAW) platform to assess the risk of heart disease. The platform employs a reflective SH-SAW sensor to reduce the sensor size and enhance the phase-shifted signals. In this study, the platform was utilized to monitor the impact of a weekly almond and oat milk or statins intervention on alterations in CVD risk. The SH-SAW ApoB test exhibited a linear range of 0 to 212 mg/dL, and a coefficient correlation (R) of 0.9912. Following a four-week intervention period, both the almond and oat milk intervention (-23.3%, p < 0.05) and statin treatment (-53.1%, p < 0.01) were observed to significantly reduce ApoB levels. These findings suggest that the SH-SAW POCT device may prove a valuable tool for monitoring CVD risk, particularly during routine daily or weekly follow-up visits.
Keywords: POCT; SH-SAW; almond; biosensor; cardiovascular disease (CVD); oat milk; statin.
Conflict of interest statement
Author C.-H.C. and H.Y. was employed by the company tst biomedical electronics Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tsao C.W., Aday A.W., Almarzooq Z.I., Alonso A., Beaton A.Z., Bittencourt M.S., Boehme A.K., Buxton A.E., Carson A.P., Commodore-Mensah Y., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145:e153–e639. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

