Post-Transplantation Seroprotection Rates in Liver, Lung, and Heart Transplant Recipients Vaccinated Pre-Transplantation against Hepatitis B Virus and Invasive Pneumococcal Disease
- PMID: 39460259
- PMCID: PMC11511315
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12101092
Post-Transplantation Seroprotection Rates in Liver, Lung, and Heart Transplant Recipients Vaccinated Pre-Transplantation against Hepatitis B Virus and Invasive Pneumococcal Disease
Abstract
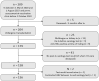
Vaccination before solid organ transplantation is recommended since post-transplantation immunosuppression is known to impair vaccine responses. However, little is known about post-transplantation seroprotection rates in organ transplant recipients vaccinated pre-transplantation. We aimed to investigate the proportion of transplant recipients vaccinated against hepatitis B virus (HBV) and invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) pre-transplantation at the time of listing for transplantation with post-transplantation seroprotection. We included 136 solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients vaccinated at the time of listing for transplantation. We investigated post-transplantation antibody concentrations against HBV and IPD. Established antibody thresholds were used to define seroprotection. The proportions of SOT recipients with post-transplantation seroprotection were 27.9% (n = 38) and 42.6% (n = 58) against HBV and IPD, respectively. Compared to completing HBV vaccination pre-transplantation, completing post-transplantation vaccination (adjusted odds ratio (aOR): 7.8, 95% CI: 2.5-24.5, p < 0.001) and incomplete vaccination (aOR: 6.3, 95% CI: 1.2-32.6, p = 0.028) were associated with non-response against HBV, after adjustment for confounders. Importantly, patients with seroprotection at the time of listing had lower odds of non-response against HBV (aOR: 0.04, 95% CI: 0.0-0.1, p < 0.001) and IPD (aOR: 0.3, 95% CI: 0.1-0.7, p = 0.007) compared to those without seroprotection. SOT recipients vaccinated pre-transplantation had low post-transplantation seroprotection rates against HBV and IPD. However, SOT recipients with seroprotection at the time of listing had lower odds of non-response, suggesting early vaccination should be a priority.
Keywords: hepatitis B; invasive pneumococcal disease; solid organ transplantation; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
L.B.H., S.R.H., A.H., L.F.L., N.E.W., L.D.H., C.E., S.B., J.G.H., I.H.M.M., P.S.K., P.N.B., M.P. and A.R. declare no conflicts of interest. Z.B.H. received research grants from Independent Research Fund (grant nr. 3162-00031B), Helen Rudes Foundation, and the Danish Cancer Society (Grant number KBVU-MS R327-A19137) not related to this work. F.G. is an advisor at Pfizer, Abbott, Ionis, Alnylam, Bayer, Astra-Zeneca, AdjuCor, and FineHeart and speaker at Novartis, all outside the current work. S.D.N. has received unrestricted research grants from the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Lundbeck Foundation, and the Independent Research Fund Denmark and reports advisory board activity for Gilead Sciences and GlaxoSmithKline/ViiV Healthcare, all unrelated to this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Nelson J., Alvey N., Bowman L., Schulte J., Segovia M.C., McDermott J., Te H.S., Kapila N., Levine D.J., Gottlieb R.L., et al. Consensus Recommendations for Use of Maintenance Immunosuppression in Solid Organ Transplantation: Endorsed by the American College of Clinical Pharmacy, American Society of Transplantation, and the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. Pharmacotherapy. 2022;42:599–633. doi: 10.1002/phar.2716. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rezahosseini O., Møller D.L., Sørensen S.S., Perch M., Gustafsson F., Gelpi M., Knudsen J., Helleberg M., Rasmussen A., Nielsen S.D., et al. An Observational Prospective Cohort Study of Incidence and Outcome of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Hemophilus influenzae Infections in Adult Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Microorganisms. 2021;9:1371. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9071371. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

