Evolution of the use, effectiveness and safety of bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection between 2013 and 2021: results from the European registry on H. pylori management (Hp-EuReg)
- PMID: 39461739
- PMCID: PMC11671959
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-332804
Evolution of the use, effectiveness and safety of bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection between 2013 and 2021: results from the European registry on H. pylori management (Hp-EuReg)
Abstract
Background: Bismuth quadruple therapies (BQTs) including bismuth, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and two antibiotics have been shown to be highly effective for treating Helicobacter pylori infection even in areas of high bacterial antibiotic resistance.
Objective: To describe the time trends of use, effectiveness and safety of BQT in Europe using the European Registry on Helicobacter pylori Management (Hp-EuReg).
Design: Patients registered in the Hp-EuReg from 2013 to 2021 who had received BQT were included. The regimens prescribed, the number of eradication attempts, effectiveness, adherence and safety were analysed. The effectiveness was assessed by modified intention to treat (mITT). Time-trend and multivariate analyses were performed to determine variables that predicted treatment success.
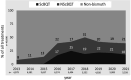
Results: Of the 49 690 patients included in the Hp-EuReg, 15 582 (31%) had received BQT. BQT use increased from 8.6% of all treatments in 2013 to 39% in 2021. Single-capsule BQT-containing bismuth, metronidazole and tetracycline-plus a PPI (single-capsule BQT, ScBQT) was the most frequent treatment mode (43%). Schemes that obtained an effectiveness above 90% were the 10-day ScBQT and 14-day BQT using tetracycline plus metronidazole, or amoxicillin plus either clarithromycin or metronidazole. Only ScBQT achieved above 90% cure rates in all the geographical areas studied. Using the ScBQT scheme, adherence, the use of standard or high-dose PPIs, 14-day prescriptions and the use of BQT as first-line treatment were significantly associated with higher mITT effectiveness.
Conclusion: The use of BQT increased notably in Europe over the study period. A 10-day ScBQT was the scheme that most consistently achieved optimal effectiveness.
Trial registration number: NCT02328131.
Keywords: ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY; HELICOBACTER PYLORI - TREATMENT; HELICOBACTER THERAPY.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: XC has received research grants and fees for lectures from Allergan. JPG has served as speaker, consultant and advisory member for or has received research funding from Mayoly Spindler, Allergan, Diasorin, Richen, Biocodex and Juvisé. OPN received research funding from Allergan, Mayoly Spindler, Richen, Biocodex and Juvisé. DSB served as a lecturer for Astellas, AstraZeneca, KRKA and Abbott. FM is a consultant for PHATHOM, DaVoltera and has received grants from Allergan, bioMerieux and Mobidiag. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
