Evaluation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) using a high figure-of-merit plasmonic multimode refractive index optical sensor
- PMID: 39462024
- PMCID: PMC11513005
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77336-3
Evaluation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) using a high figure-of-merit plasmonic multimode refractive index optical sensor
Abstract
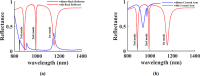
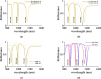
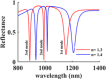
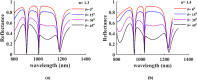
In recent years, following the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a significant increase in cases of SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2) and related deaths worldwide. Despite the pandemic nearing its end due to the introduction of mass-produced vaccines against SARS-CoV-2, early detection and diagnosis of the virus remain crucial in preventing disease progression. This article explores the rapid identification of SARS-CoV-2 by implementing a multimode plasmonic refractive index (MMRI) optical sensor, developed based on the split ring resonator (SRR) design. The Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) numerical solution method simulates the sensor. The studied sensor demonstrates three resonance modes within the reflection spectrum ranging from 800 nm to 1400 nm. Its material composition and dimensional parameters are optimized to enhance the sensor's performance. The research indicates that all three resonance modes exhibit strong performance with high sensitivity and figures of merit. Notably, the first mode achieves an exceptional sensitivity of 557 nm/RIU, while the third mode exhibits a commendable sensitivity of 453 nm/RIU and a Figure of Merit (FOM) of 45 RIU-1. These findings suggest that the developed MMRI optical sensor holds significant potential for the early and accurate detection of SARS-CoV-2, contributing to improved disease management and control efforts.
Keywords: Multimode refractive index (MMRI); Optical sensor; SARS-CoV-2; Sensitivity; Split ring resonator (SRR).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Weiss, C. et al. Toward nanotechnology-enabled approaches against the COVID-19 pandemic. ACS nano. 14 (6), 6383–6406 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Chamola, V. et al. A comprehensive review of the COVID-19 pandemic and the role of IoT, drones, AI, blockchain, and 5G in managing its impact. Ieee Access.8, 90225–90265 (2020).
-
- Bajaj, A. et al. Synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for SARS-CoV-2 virus detection using surface plasmon resonance. Chemosensors. 10 (11), 459 (2022).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

