Caffeic acid inhibits Staphylococcus aureus-induced endometritis through regulating AMPKα/mTOR/HIF-1α signalling pathway
- PMID: 39462269
- PMCID: PMC11512753
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70175
Caffeic acid inhibits Staphylococcus aureus-induced endometritis through regulating AMPKα/mTOR/HIF-1α signalling pathway
Abstract
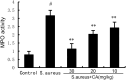
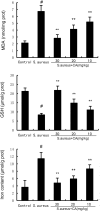
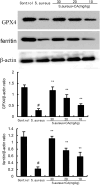
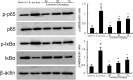
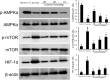
Endometritis is mostly caused by childbirth or postpartum uterine infection. It is one of the important reasons leading to female infertility. Caffeic acid (CA) and its derivatives are widely found in some foods and traditional Chinese medicine, and have biological activities such as antioxidant, free radical scavenging, anti-inflammatory, and anti-infection. In this study, we aimed to explore the effect of CA on Staphylococcus aureus-induced endometritis. The contents of TNF-α and IL-1β were detected by ELISA in S. aureus-induced endometritis model. Western blot assay was used to detect the expression of AMPKα/mTOR/HIF-1α pathway related proteins and GPX4 expression. In addition, the concentrations of MDA, GSH, and iron were tested by the assay kits. Compared with the model group, CA treatment significantly alleviated S. aureus-induced uterine injury, MPO activity, the contents of inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-1β, and NF-κB activation. Meanwhile, CA significantly inhibited S. aureus-induced ferroptosis, as confirmed by decreased MDA and iron concentration and up-regulated GPX4 expression and GSH level. Furthermore, CA attenuated S. aureus-induced HIF-1α and phosphorylated mTOR expression and increased phosphorylated AMPK expression. In conclusion, CA inhibits inflammation and ferroptosis by regulating AMPKα/mTOR/HIF-1α signalling pathway to alleviate S. aureus-induced endometritis in mice.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; AMPK; endometritis; ferroptosis; inflammation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non‐financial interests to disclose.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

