Virologically suppressed switch to Dolutegravir/Lamivudine 2-Drug regimen versus switch to commonly prescribed 3-Drug regimens in the United States
- PMID: 39462377
- PMCID: PMC11515283
- DOI: 10.1186/s12981-024-00668-7
Virologically suppressed switch to Dolutegravir/Lamivudine 2-Drug regimen versus switch to commonly prescribed 3-Drug regimens in the United States
Abstract
Background: Two-drug regimens (2DRs) have been introduced in recent years to potentially reduce antiretroviral therapy (ART) toxicities and drug-drug interactions while demonstrating comparable efficacy to three-drug regimens (3DRs) for people with HIV (PWH). The objective of this study was to compare the real-world effectiveness and durability of a single-tablet 2DR of dolutegravir/lamivudine (DTG/3TC) with that of commonly prescribed 3DRs in ART-experienced, virologically suppressed PWH during the first 24 months of DTG/3TC availability in the United States.
Methods: Virologically suppressed (viral load [VL] < 200 copies/mL) adult PWH initiating DTG/3TC 2DR, bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (BIC/FTC/TAF), or a DTG-based 3DR between 01MAY2019 and 31OCT2020 were identified in the OPERA® cohort and followed through 30APR2021. Univariate Poisson regression (incidence rates) and marginal structural Cox proportional hazards models with inverse probability of treatment weights (hazard ratios) were used to quantify relationships between regimen type and confirmed virologic failure (2 consecutive VLs ≥ 200 copies/mL) or regimen discontinuation. Reasons for discontinuation were examined.
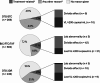
Results: A total of 8,037 ART-experienced, virologically suppressed PWH met the inclusion criteria and switched to DTG/3TC (n = 1,450), BIC/FTC/TAF (n = 5,691), or a DTG-based 3DR (n = 896). Incidence rates of confirmed virologic failure were low for all groups, at 0.66 (DTG/3TC), 0.84 (BIC/FTC/TAF), and 1.78 (DTG 3DR) per 100 person-years (py). Compared to DTG/3TC, only the DTG 3DRs were associated with a statistically significant increased hazard of confirmed virologic failure (hazard ratio: 5.21, 95% confidence interval: 1.85, 14.67). Discontinuation rates per 100 py were highest in the DTG 3DR group (24.90), followed by the DTG/3TC group (17.69) and the BIC/FTC/TAF group (8.30). Regardless of regimen, discontinuations were infrequently attributed to effectiveness (VL ≥ 200 copies/mL; 4%) or tolerability (adverse diagnoses, side effects, or lab abnormalities; 6%).
Conclusions: Among virologically suppressed PWH initiating a new regimen, few individuals experienced virologic failure in real-world clinical care. While rates of regimen discontinuation were high, most discontinuations could not be attributed to a lack of virologic control or poor tolerability. These findings suggest that DTG/3TC is an effective option for ART-experienced, virologically suppressed PWH.
Keywords: 2-drug regimen; 3-drug regimen; Antiretroviral therapy; Bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide; Cohort; Dolutegravir; Dolutegravir/lamivudine; Effectiveness; HIV.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
GP, MBW, and AM are members of the Epidemiology and Clinical Advisory Board for Epividian. MBW has participated in post-conference advisory boards for the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections and International AIDS Conference and serves as a principal investigator on ViiV Healthcare clinical trials but does not receive personal compensation for this work, which goes directly to the AIDS Healthcare Foundation. AM receives research funding from Gilead, ViiV, GSK, Abbott, Roche, and Merck. He has attended advisory boards for Gilead, ViiV, and Epividian. JSF, LB, and GPF are employed by Epividian, Inc.; Epividian has had research funded by ViiV Healthcare, Merck & Co., Janssen, Gilead Sciences, Theratechnologies, EMD Serono, and AIDS Healthcare Foundation. VV, SS, CEH, and JvW are employed by ViiV Healthcare and hold stock in GSK as part of their employment.
Figures

References
-
- Ballantyne AD, Perry CM. Dolutegravir: first global approval. Drugs. 2013;73(14):1627–37. - PubMed
-
- Markham A. Bictegravir: first global approval. Drugs. 2018;78:601–6. - PubMed
-
- Teeraananchai S, Kerr S, Amin J, Ruxrungtham K, Law M. Life expectancy of HIV-positive people after starting combination antiretroviral therapy: a meta-analysis. HIV Med. 2017;18(4):256–66. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

