Effects of Glaucoma Treatment on Ocular Surface and Tear Functions: Comparison of Trabeculectomy and Antiglaucoma Drops
- PMID: 39463149
- PMCID: PMC11589238
- DOI: 10.4274/tjo.galenos.2024.39277
Effects of Glaucoma Treatment on Ocular Surface and Tear Functions: Comparison of Trabeculectomy and Antiglaucoma Drops
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate tear function and ocular surface disease (OSD) findings in patients with glaucoma who received antiglaucoma medication in one eye and trabeculectomy surgery in the other eye.
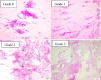
Materials and methods: The patient group included 38 eyes of 19 patients who had undergone trabeculectomy surgery with mitomycin C (MMC) treatment in one eye at least 6 months prior. These eyes were followed up without medication while the fellow eye continued receiving antiglaucomatous medication. The control group comprised 20 eyes of 20 healthy individuals. Demographic data, follow-up period after trabeculectomy, antiglaucoma medications, number of drops per day, and duration of medication were recorded. Tear break-up time (BUT), corneal and conjunctival fluorescein staining, Schirmer II test, and conjunctival impression cytology were performed.
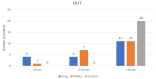
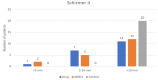
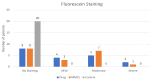
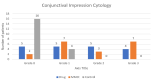
Results: A statistically significant difference was observed in BUT, corneal and conjunctival fluorescein staining, Schirmer II test, and Nelson staging levels in both eyes of patients with glaucoma compared to the control group (p=0.05). Although not statistically significant, BUT, Schirmer II test, punctate staining, and Nelson staging results showed improvement with increasing postoperative time.
Conclusion: In our patient group, antiglaucoma medications and trabeculectomy surgery with MMC induced OSD to a similar degree. No superiority was observed between trabeculectomy with MMC and antiglaucoma drops in terms of OSD incidence.
Amaç: Bir gözüne antiglokomatöz ilaç tedavisi ve diğer gözüne trabekülektomi cerrahisi uygulanan glokom hastalarında gözyaşı fonksiyonu ve oküler yüzey hastalığı (OYH) bulgularını araştırmak.
Gereç ve Yöntem: Hasta grubu, bir gözüne en az 6 ay önce mitomisin C (MMC) uygulamalı trabekülektomi ameliyatı yapılıp ilaçsız takip edilen ve diğer gözüne antiglokomatöz ilaç kullanan 19 hastanın 38 gözünden oluşmaktaydı. Kontrol grubu olarak 20 sağlıklı bireyin 20 gözü çalışmaya dahil edildi. Demografik veriler, trabekülektomi sonrası takip süresi, antiglokomatöz ilaçlar, günlük damla sayısı ve ilaç kullanım süresi kaydedildi. Gözyaşı kırılma zamanı (GKZ), korneal ve konjonktival floresein boyama, Schirmer II testi ve konjonktival impresyon sitolojisi yapıldı.
Bulgular: Glokom hastalarının her iki gözünde GKZ, korneal ve konjonktival floresein boyanması, Schirmer II testi ve Nelson evreleme düzeylerinde kontrol grubuna göre istatistiksel olarak anlamlı fark vardı (p=0,05). İstatistiksel olarak anlamlı olmamakla birlikte, ameliyat sonrası süre arttıkça GKZ, Schirmer II testi, punktat boyanma ve Nelson evreleme sonuçlarının daha iyi olduğu bulundu.
Sonuç: Glokom hastalarında kullanılan ilaçlar ve MMC ile trabekülektomi cerrahisi hasta grubumuzda benzer şiddette OYH’ye neden oldu. OYH insidansı açısından MMC ile trabekülektomi ve antiglokomatöz ilaçlar arasında bir üstünlük yoktu.
Keywords: Antiglaucoma drugs; conjunctival impression cytology; glaucoma; ocular surface disease; trabeculectomy.
©Copyright 2024 by the Turkish Ophthalmological Association / Turkish Journal of Ophthalmology published by Galenos Publishing House.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Nelson JD, Havener VR, Cameron JD. Cellulose acetate impressions of the ocular surface. Dry eye states. Arch Ophthalmol. 1983;101:1869–1872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
