In Vitro Efficacy of Domestic Techniques for Disinfection of Toothbrushes Contaminated With Enterococcus faecalis
- PMID: 39463490
- PMCID: PMC11511586
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/3509832
In Vitro Efficacy of Domestic Techniques for Disinfection of Toothbrushes Contaminated With Enterococcus faecalis
Abstract
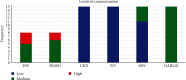
Introduction: Oral hygiene education for patients is fundamental in preventive-promotional dentistry. The disinfection of toothbrushes (TBs) must be integrated into this context due to their proximity to contaminant sources that make them vulnerable to cross infection in homes. The objective of this study was to compare the efficacy of domestic techniques for disinfection of TBs. Materials and Methods: We performed an in vitro study of 76 TBs contaminated with Enterococcus faecalis (Ef) ATCC 29212 subjected to different disinfection protocols: G1. Distilled water (DW; negative control; n = 8), G2. Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)10% (negative control; n = 8), G3. Chlorhexidine (CHX) 0.12% (positive control; n = 15), G4. 100% white vinegar (WV; n = 15), G5. Microwave (MW) at 700 W (n = 15), and G6. 200 mg/mL of certified alcoholic extract of purple garlic (GARLIC) from Arequipa (Allium sativum L; n = 15). Bacterial count was assessed by colony-forming units (CFU/mL) categorized as contamination: low (<30), medium (30-300), and high (>300). The Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc pairs was used at a significance level of p < 0.05. Results: Efficacy against Ef showed highly significant differences between groups (p < 0.001) with lower median CFU/mL in G3 and G4 (Me = 0 [IQR (interquartile range) = 0]: low) and G5 (Me = 6000 [IQR = 45,000]: low/medium) versus negative controls (Me = 378,500 and 5,020,000 [IQR = 4,605,000 and 6,760,000]: medium/high; p ≤ 0.019). The counts of the G5 were not statistically different than G3, G4, and G6 (p > 0.06). The G6 (Me = 1,510,000 [IQR = 590,000]: medium) was inferior to G3 and G4 (p < 0.001), but similar to both negative control groups (p > 0.999). Conclusions: Disinfection of TBs with CHX, WV, and MWs produces a significant effective reduction in the count of Ef.
Keywords: Allium sativum; disinfection; microwave; toothbrush; vinegar.
Copyright © 2024 Gina Alessandra Donayre-Salvatierra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jathar P., Panse A., Desai A. R. Comparative Evaluation of Various Disinfectant Agents to Disinfect Toothbrush Microbiota. International Journal of Pedodontic Rehabilitation . 2018;3(1):12–17. doi: 10.4103/ijpr.ijpr_11_17. - DOI
-
- Yactayo-Alburquerque M. T., Alen-Méndez M. L., Azañedo D., Comandé D., Hernández-Vásquez A. Impact of Oral Diseases on Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Systematic Review of Studies Conducted in Latin America and the Caribbean. PLOS ONE . 2021;16(6) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252578.e0252578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klonowicz D., Czerwinska M., Sirvent A., Gatignol J.-P. A New Tooth Brushing Approach Supported by an Innovative Hybrid Toothbrush-Compared Reduction of Dental Plaque After a Single use Versus an Oscillating-Rotating Powered Toothbrush. BMC Oral Health . 2018;18(1) doi: 10.1186/s12903-018-0647-7.185 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

