This is a preprint.
Identification of SLC35A1 as an essential host factor for the transduction of multi-serotype recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors
- PMID: 39463973
- PMCID: PMC11507909
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.10.16.618764
Identification of SLC35A1 as an essential host factor for the transduction of multi-serotype recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors
Update in
-
Identification of SLC35A1 as an essential host factor for the transduction of multi-serotype recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors.mBio. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):e0326824. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03268-24. Epub 2024 Nov 27. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39601564 Free PMC article.
Abstract
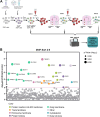
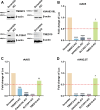
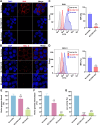
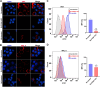
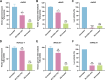
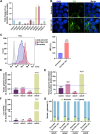
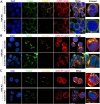
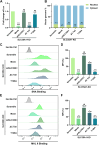
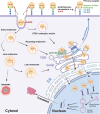
We conducted a genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screen in suspension 293-F cells transduced with rAAV5. The highly selected genes revealed after two rounds of screens included the previously reported KIAA039L, TM9SF2, and RNF121, along with a cluster of genes involved in glycan biogenesis, Golgi apparatus localization and endoplasmic reticulum penetration. In this report, we focused on solute carrier family 35 member A1 (SLC35A1), a Golgi apparatus-localized cytidine 5'-monophosphate-sialic acid (CMP-SIA) transporter. We confirmed that SLC35A1 knockout (KO) significantly decreased rAAV5 transduction to a level lower than that observed in KIAA0319L or TM9SF2 KO cells. Although SLC35A1 KO drastically reduced the expression of α2,6-linked SIA on the cell surface, the expression of α2,3-linked SIA, as well as the cell binding and internalization of rAAV5, were only moderately affected. Moreover, SLC35A1 KO significantly diminished the transduction of AAV multi-serotypes, including rAAV2 and rAAV3 which do not utilize SIAs for primary attachment. Notably, the SLC35A1 KO markedly increased transduction of rAAV9 and rAAV11, which primarily attach to cells via binding to galactose. Further analyses revealed that SLC35A1 KO significantly decreased vector nuclear import. More importantly, although the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail deletion (ΔC Tail) mutant of SLC35A1 did not drastically decrease SIA expression, it significantly decreased rAAV transduction, as well as vector nuclear import, suggesting the C-tail is critical in these processes. Furthermore, the T128A mutant significantly decreased SIA expression, but still supported rAAV transduction and nuclear import. These findings highlight the involvement of the CMP-SIA transporter in the intracellular trafficking of rAAV vectors post-internalization.
Keywords: SLC35A1; intracellular trafficking; nuclear import; rAAV; transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST RM is an employee of GeneGoCell Inc. The remaining authors have no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of SLC35A1 as an essential host factor for the transduction of multi-serotype recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors.mBio. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):e0326824. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03268-24. Epub 2024 Nov 27. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39601564 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Host Restriction Factors Critical for Recombinant AAV Transduction of Polarized Human Airway Epithelium.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 27:2023.09.27.559795. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.27.559795. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Virol. 2023 Dec 21;97(12):e0133023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01330-23. PMID: 37808760 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Cytidine Monophosphate N-Acetylneuraminic Acid Synthetase and Solute Carrier Family 35 Member A1 Are Required for Reovirus Binding and Infection.J Virol. 2020 Dec 22;95(2):e01571-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01571-20. Print 2020 Dec 22. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 33087464 Free PMC article.
-
An interaction between SLC35A1 and ST3Gal4 is differentially affected by CDG-causing mutations in the SLC35A1 gene.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Dec 20;635:46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.10.019. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36257191
-
Structural and cellular biology of adeno-associated virus attachment and entry.Adv Virus Res. 2020;106:39-84. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2020.01.002. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Adv Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32327148 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
