This is a preprint.
Efficient multiplex non-viral engineering and expansion of polyclonal γδ CAR-T cells for immunotherapy
- PMID: 39464114
- PMCID: PMC11507710
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.03.611042
Efficient multiplex non-viral engineering and expansion of polyclonal γδ CAR-T cells for immunotherapy
Abstract
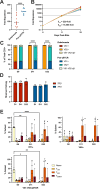
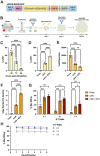
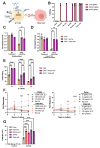
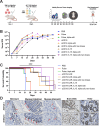
Gamma delta (γδ) T cells are defined by their unique ability to recognize a limited repertoire of non-peptide, non-MHC-associated antigens on transformed and pathogen-infected cells. In addition to their lack of alloreactivity, γδ T cells exhibit properties distinct from other lymphocyte subsets, prompting significant interest in their development as an off-the-shelf cellular immunotherapeutic. However, their low abundance in circulation, heterogeneity, limited methods for ex vivo expansion, and under-developed methodologies for genetic modification have hindered basic study and clinical application of γδ T cells. Here, we implement a feeder-free, scalable approach for ex vivo manufacture of polyclonal, non-virally modified, gene edited chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-γδ T cells in support of therapeutic application. Engineered CAR-γδ T cells demonstrate high function in vitro and and in vivo. Longitudinal in vivo pharmacokinetic profiling of adoptively transferred polyclonal CAR-γδ T cells uncover subset-specific responses to IL-15 cytokine armoring and multiplex base editing. Our results present a robust platform for genetic modification of polyclonal CAR-γδ T cells and present unique opportunities to further define synergy and the contribution of discrete, engineered CAR-γδ T cell subsets to therapeutic efficacy in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests B.S.M. and B.R.W. have filed patents have been filed relating to the methods and approaches outlined in this manuscript and are founders and hold equity in Luminary Therapeutics who have licensed this IP.
Figures
References
-
- Davis M. M. & Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature 334, 395–402 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Constant P. et al. Stimulation of human gamma delta T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science 264, 267–270 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Tanaka Y. et al. Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human gamma delta T cells. Nature 375, 155–158 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Fournié J. J. & Bonneville M. Stimulation of gamma delta T cells by phosphoantigens. Res. Immunol. 147, 338–347 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
