Impact of whole-body and skeletal muscle composition on peak oxygen uptake in heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39464232
- PMCID: PMC11505452
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeae082
Impact of whole-body and skeletal muscle composition on peak oxygen uptake in heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
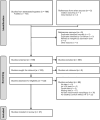
Aims: Heart failure (HF) has a major impact on exercise tolerance that may (in part) be due to abnormalities in body and skeletal muscle composition. This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to assess how differences in whole-body and skeletal muscle composition between patients with HF and non-HF controls (CON) contribute to reduced peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak).
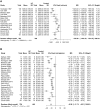
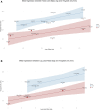
Methods and results: The PubMed database was searched from 1975 to May 2024 for eligible studies. Cross-sectional studies with measures of VO2peak, body composition, or muscle biopsies in HF and CON were considered. Out of 709 articles, 27 studies were included in this analysis. Compared with CON, VO2peak [weighted mean difference (WMD): -9.96 mL/kg/min, 95% confidence interval (CI): -11.71 to -8.21), total body lean mass (WMD: -1.63 kg, 95% CI: -3.05 to -0.21), leg lean mass (WMD: -1.38 kg, 95% CI: -2.18 to -0.59), thigh skeletal muscle area (WMD: -10.88 cm2 , 95% CI: -21.40 to -0.37), Type I fibres (WMD: -7.76%, 95% CI: -14.81 to -0.71), and capillary-to-fibre ratio (WMD: -0.27, 95% CI: -0.50 to -0.03) were significantly lower in HF. Total body fat mass (WMD: 3.34 kg, 95% CI: 0.35-6.34), leg fat mass (WMD: 1.37 kg, 95% CI: 0.37-2.37), and Type IIx fibres (WMD: 7.72%, 95% CI: 1.52-13.91) were significantly higher in HF compared with CON. Absolute VO2peak was significantly associated with total body and leg lean mass, thigh skeletal muscle area, and capillary-to-fibre ratio.
Conclusion: Individuals with HF display abnormalities in body and skeletal muscle composition including reduced lean mass, oxidative Type I fibres, and capillary-to-fibre ratio that negatively impact VO2peak.
Keywords: Body composition; Exercise intolerance; Heart failure; Peak oxygen uptake; Skeletal muscle.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures



References
-
- Del Buono MG, Arena R, Borlaug BA, Carbone S, Canada JM, Kirkman DL, Garten R, Rodriguez-Miguelez P, Guazzi M, Lavie CJ, Abbate A. Exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;73:2209–2225. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan MJ, Green HJ, Cobb FR. Skeletal muscle biochemistry and histology in ambulatory patients with long-term heart failure. Circulation 1990;81:518–527. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

