Efferocytosis dysfunction in CXCL4-induced M4 macrophages: phenotypic insights in systemic sclerosis in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 39464886
- PMCID: PMC11512447
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1468821
Efferocytosis dysfunction in CXCL4-induced M4 macrophages: phenotypic insights in systemic sclerosis in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Introduction: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune disease characterized by antinuclear antibody production, which has been linked to an excess of apoptotic cells, normally eliminated by macrophages through efferocytosis. Additionally, circulating levels of CXCL4, a novel SSc biomarker, correlate with more severe fibrotic manifestations of the disease. Considering the defective efferocytosis of macrophages in SSc and the CXCL4-related M4 macrophage phenotype, we hypothesized that CXCL4 could be involved in the alteration of phagocytic functions of macrophages in SSc, including LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP), another phagocytic process requiring autophagy proteins and contributing to immune silencing.
Methods: In this study, CXCL4 levels were measured by ELISA in vitro in the serum of SSc patients, and also in vivo in the serum and lungs of C57BL/6J SSc mice induced by intradermal injections of hypochloric acid (HOCl) or Bleomycin (BLM), with evaluation of M4 markers. Circulating monocytes from healthy donors were also differentiated in vitro into M4 monocytes-derived macrophages (MDMs) in the presence of recombinant CXCL4. In M4-MDMs, phagocytosis of fluorescent beads and expression level of efferocytic receptors were evaluated by flow cytometry in vitro, while efferocytosis of pHrodo-stained apoptotic Jurkat cells was evaluated by real-time fluorescence microscopy. LAP quantification was made by fluorescence microscopy in M4-MDMs exposed to IgG-coated beads as well as apoptotic Jurkat cells.
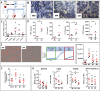
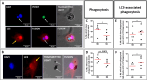
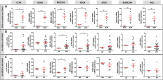
Results: Our results demonstrated that efferocytosis was significantly reduced in M0-MDMs from healthy donors exposed to the CXCL4-rich plasma of SSc patients. In vivo, CXCL4 expression was increased in the lungs of both SSc-mouse models, along with elevated M4 markers, while efferocytosis of BLM-mice alveolar macrophages was decreased. In vitro, M4-MDMs exhibited reduced efferocytosis compared to M0-MDMs, notably attributable to lower CD36 receptor expression and impaired phagocytosis capacities, despite enhanced LAP. Autophagic gene expression was increased both in vitro in SSc MDMs and in vivo in BLM mice, thus acting as a potential compensatory mechanism.
Discussion: Altogether, our results support the role of CXCL4 on the impaired efferocytosis capacities of human macrophages from SSc patients and in SSc mice.
Keywords: CXCL4; efferocytosis; fibrosis; macrophage; phagocytosis; systemic sclerosis.
Copyright © 2024 Le Tallec, Bellamri, Lelong, Morzadec, Frenger, Ballerie, Cazalets, Lescoat, Gros and Lecureur.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

