Partial reduction of interleukin-33 signaling improves senescence and renal injury in diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 39465143
- PMCID: PMC11502718
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.742
Partial reduction of interleukin-33 signaling improves senescence and renal injury in diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
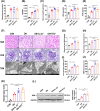
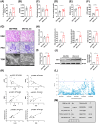
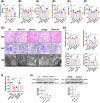
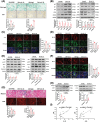
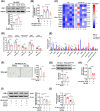
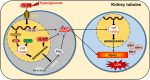
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a frequent and costly complication of diabetes with limited understandings of mechanisms and therapies. Emerging evidence points to the important roles of interleukin-33 (IL-33) in acute kidney injury, yet its contribution to DN is still unclear. We here found a ubiquitous increase of IL-33 and its receptor (ST2) in murine models and patients with DN. Surprisingly, both IL-33 and ST2 knockdown aggravated renal lesions in DN, while overexpression of IL-33 also exacerbated the condition. Further population-based analyses revealed a positive correlation of IL-33 expression with renal dysfunction in DN patients. Individuals with high IL-33 expression-related polygenic risk score had a higher DN risk. These findings confirmed the harmful effects of IL-33 on DN. Conversely, endogenous and exogenous partial reduction of IL-33 signaling conferred renoprotective effects in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistically, IL-33 induced senescence by regulating cell cycle factors in HK-2 cells, and accordingly senescence led to renal cell damage through the secretion of senescence-related secretory phenotype (SASP) including IL-33 and prostaglandins. Together, elevated IL-33 accelerates cellular senescence to drive DN possibly by SASP production, while a partial blockage improves renal injury and senescence. Our findings pinpoint a possible and new avenue for DN interventions.
Keywords: cellular senescence; diabetic nephropathy; interleukin‐33; senescence‐related secretory phenotype.
© 2024 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tuttle KR, Agarwal R, Alpers CE, et al. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2022;102(2):248‐260. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Reeves WB, Awad AS. Pathophysiology of diabetic kidney disease: impact of SGLT2 inhibitors. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021;17(5):319‐334. - PubMed
-
- Cayrol C, Girard JP. Interleukin‐33 (IL‐33): a nuclear cytokine from the IL‐1 family. Immunol Rev. 2018;281(1):154‐168. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
