Reproducibility of 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) contrasts in the healthy brain at 3T
- PMID: 39465319
- PMCID: PMC11514173
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-75777-4
Reproducibility of 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) contrasts in the healthy brain at 3T
Abstract
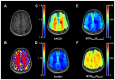
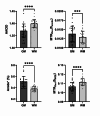
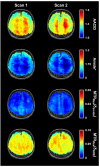
Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging may provide novel contrast for the diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of the progression or treatment of neurological applications. However, the reproducibility of prominent CEST contrasts like amide CEST and nuclear Overhauser enhancement (NOE) CEST must be characterized in healthy brain gray matter (GM) and white matter (GM) prior to clinical implementation. The objective of this study was to characterize the reproducibility of four different CEST contrasts in the healthy human brain. Using a 3T MRI scanner, two 3D CEST scans were acquired in 12 healthy subjects (7 females, mean age (± SD) 26 ± 4 years) approximately 10 days apart. Scan-rescan reproducibility was measured for four contrasts: amine/amide concentration-independent detection (AACID), Amide*, and inverse magnetization transfer ratio (MTRRex) contrast for amide and NOE. Reproducibility was evaluated between- and within-subjects using coefficients of variation (CV) and the percent difference between measurements. AACID and NOE-MTRRex contrasts demonstrated the lowest within-subject CVs (0.8-1.2% and 1.6-2.0%, respectively), between-subject CVs (1.2-2.1% and 3.4-4.2%, respectively), and percent difference (1.2-1.4% and 2.2-2.8%, respectively) for both GM and WM. AACID and NOE-MTRRex contrasts demonstrated the highest reproducibility and represented stable measurements suitable for characterizing changes in brain tissue caused by pathological processes.
Keywords: Amide; CEST MRI; Gray matter; Nuclear overhauser enhancement; Reproducibility; White matter.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.E.C., S.A.D., N.D., and R.B. report no disclosures. P.L. is currently employed by Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Germany.
Figures



Similar articles
-
3D gradient echo snapshot CEST MRI with low power saturation for human studies at 3T.Magn Reson Med. 2019 Apr;81(4):2412-2423. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27569. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Magn Reson Med. 2019. PMID: 30431179 Free PMC article.
-
Is there any difference in Amide and NOE CEST effects between white and gray matter at 7T?J Magn Reson. 2016 Nov;272:82-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Sep 16. J Magn Reson. 2016. PMID: 27662404
-
Reproducibility of 3D pH-weighted chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast in the healthy cervical spinal cord.NMR Biomed. 2024 May;37(5):e5103. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5103. Epub 2024 Jan 19. NMR Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38243648
-
Magnetization Transfer Contrast and Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer MRI. Features and analysis of the field-dependent saturation spectrum.Neuroimage. 2018 Mar;168:222-241. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.04.045. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28435103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging and its main and potential applications in pre-clinical and clinical studies.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2019 Oct;9(10):1747-1766. doi: 10.21037/qims.2019.10.03. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2019. PMID: 31728316 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted MR Imaging and Signal Variations in a Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy.Metabolites. 2025 Jul 9;15(7):465. doi: 10.3390/metabo15070465. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40710565 Free PMC article.
-
The Pulseq-CEST Library: definition of preparations and simulations, example data, and example evaluations.MAGMA. 2025 Jul;38(3):413-422. doi: 10.1007/s10334-025-01242-6. Epub 2025 Mar 27. MAGMA. 2025. PMID: 40146474 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

