Microfibrillar-associated protein 4 as a predictive biomarker of treatment response in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases initiating biologics: secondary analyses based on the prospective BELIEVE cohort study
- PMID: 39465398
- PMCID: PMC11618207
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-024-05744-9
Microfibrillar-associated protein 4 as a predictive biomarker of treatment response in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases initiating biologics: secondary analyses based on the prospective BELIEVE cohort study
Abstract
Background: Currently, there are no reliable biomarkers for predicting treatment response in chronic inflammatory diseases (CIDs).
Objective: To determine whether serum microfibrillar-associated protein 4 (MFAP4) levels can predict the treatment response to biological therapy in patients with CIDs.
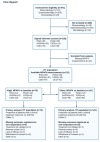
Methods: The BELIEVE study was originally designed as a prospective, multi-center cohort study of 233 patients with either rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, axial spondyloarthritis, Crohn's disease, or ulcerative colitis, initiating treatment with a biologic agent (or switching to another). Clinical assessment and blood sample collection were performed at baseline and 14-16 weeks after treatment initiation. The primary analyses included participants with available blood samples at baseline; missing data were handled as non-responders. The patients were stratified into the upper tertile of serum MFAP4 (High MFAP4) versus a combined category of middle and lower tertiles (Other MFAP4). The primary outcome was the proportion of patients with clinical response to biologic therapy after 14-16 weeks.
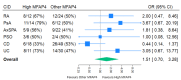
Results: 211 patients were included in the primary analysis population. The mean age was 43.7 (SD: 14.8) years, and 120 (59%) were female. Positive treatment response was observed in 41 (59%) and 69 (49%) for High MFAP4 and Other MFAP4, respectively. When adjusting for pre-specified variables (CID, age, sex, smoking status, and BMI), the adjusted OR was 2.28 (95% CI: 1.07 to 4.85) for a positive treatment outcome in the High MFAP4 group.
Conclusion: A high MFAP4 status before initiating biological treatment is associated with a positive clinical response, when adjusting for confounding factors.
Keywords: Axial spondyloarthritis; Biologic treatment; Chronic inflammatory disease; Crohn’s disease; MFAP4; Psoriasis; Psoriatic arthritis; Rheumatoid arthritis; Treatment response; Ulcerative colitis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Disclaimer: This study is part of a PhD thesis, and some of the main findings of this study have been presented in the PhD thesis. The thesis can be accessed here: Bjork.K.Sofiudottir_rsyd.dk.pdf_reduced.pdf (sdu.dk). Competing interests: The authors report no conflict of interest in relation to this study. BKS reports a congress-fee grant from Boehringer-Ingelheim, and JRD reports that he received teaching fees, congress-fee grants, and research grant from Boehringer-Ingelheim for another study.
Figures
References
-
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N et al (2017) Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet (London England) 390(10114):2769–2778 - PubMed
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D et al (2014) The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis 73(7):1316–1322 - PubMed
-
- Knowles SR, Graff LA, Wilding H, Hewitt C, Keefer L, Mikocka-Walus A (2018) Quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and Meta-analyses-part I. Inflamm Bowel Dis 24(4):742–751 - PubMed
-
- Hyldgaard C, Hilberg O, Pedersen AB et al (2017) A population-based cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: comorbidity and mortality. Ann Rheum Dis 76(10):1700–1706 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

