Diagnosis of schizophrenia by integrated saccade scores and associations with psychiatric symptoms, and functioning
- PMID: 39465854
- PMCID: PMC11479490
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039935
Diagnosis of schizophrenia by integrated saccade scores and associations with psychiatric symptoms, and functioning
Abstract
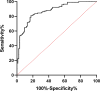
Eye movement as a neurobiological biomarker of schizophrenia. We aim to estimate diagnostic accuracy of integrated pro/antisaccade eye movement measurements to discriminate between healthy individuals and schizophrenic patients. We compared the eye movement performance of 85 healthy individuals and 116 schizophrenia-stable patients during prosaccade and antisaccade tasks. The difference eye movement measurements were accumulated by stepwise discriminant analysis to produce an integrated score. Finally, the diagnostic value of the integrated score was calculated by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) area under the curve (AUC), and the best sensitivity and specificity were calculated based on the given cutoff values. Using discriminant analysis, an integrated score included the residual gain and latency (step) during the prosaccade test, the error rate, and the corrected error rate during the antisaccade test. We found that the integrated score could well classify schizophrenia patients and healthy individuals with an accuracy of 80.6%. In the ROC, Youden's index was 0.634 (sensitivity = 81.0%, specificity = 82.4%) and AUC was 0.871. There were significant difference patterns of correlation between the severity of psychiatric symptoms and daily functioning and diagnostic eye movement measurements. Using only 2 saccade tasks to discriminate well between schizophrenia patients and healthy controls, suggesting that abnormalities in saccade behavior is a potential biomarker and efficient diagnostic tool for identifying schizophrenia. The underlying neuropathologic mechanisms associated with abnormal saccades may provide insights into the intervention and diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Huang Y, Wang Y, Wang H, et al. . Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6:211–24. - PubMed
-
- Gaebel W, Zielasek J. Schizophrenia in 2020: trends in diagnosis and therapy. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015;69:661–73. - PubMed
-
- Larsen TK, Melle I, Auestad B, et al. . Early detection of psychosis: positive effects on 5-year outcome. Psychol Med. 2011;41:1461–9. - PubMed
-
- Cattarinussi G, Kubera KM, Hirjak D, Wolf RC, Sambataro F. Neural correlates of the risk for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a meta-analysis of structural and functional neuroimaging studies. Biol Psychiatry. 2022;92:375–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

