Software-assisted structured reporting and semi-automated TNM classification for NSCLC staging in a multicenter proof of concept study
- PMID: 39466506
- PMCID: PMC11519274
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-024-01836-z
Software-assisted structured reporting and semi-automated TNM classification for NSCLC staging in a multicenter proof of concept study
Abstract
Objectives: In this multi-center study, we proposed a structured reporting (SR) framework for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and developed a software-assisted tool to automatically translate image-based findings and annotations into TNM classifications. The aim of this study was to validate the software-assisted SR tool for NSCLC, assess its potential clinical impact in a proof-of-concept study, and evaluate current reporting standards in participating institutions.
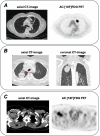
Methods: A framework for SR and staging of NSCLC was developed in a multi-center collaboration. SR annotations and descriptions were used to generate semi-automated TNM classification. The SR and TNM classification tools were evaluated by nine radiologists on n = 20 representative [18F]FDG PET/CT studies and compared to the free text reporting (FTR) strategy. Results were compared to a multidisciplinary team reference using a generalized linear mixed model (GLMM). Additionally, participants were surveyed on their experience with SR and TNM classification.
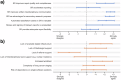
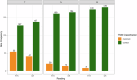
Results: Overall, GLMM analysis revealed that readers using SR were 1.707 (CI: 1.137-2.585) times more likely to correctly classify TNM status compared to FTR strategy (p = 0.01) resulting in increased overall TNM correctness in 71.9% (128/178) of cases compared to 62.8% (113/180) FTR. The primary source of variation in classification accuracy was explained by case complexity. Participants rated the potential impact of SR and semi-automated TNM classification as positive across all categories with improved scores after template validation.
Conclusion: This multi-center study yielded an effective software-assisted SR framework for NSCLC. The SR and semi-automated classification tool improved TNM classification and were perceived as valuable.
Critical relevance statement: Software-assisted SR provides robust input for semi-automated rule-based TNM classification in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), improves TNM correctness compared to FTR, and was perceived as valuable by radiology physicians.
Key points: SR and TNM classification are underutilized across participating centers for NSCLC staging. Software-assisted SR has emerged as a promising strategy for oncologic assessment. Software-assisted SR facilitates semi-automated TNM classification with improved staging accuracy compared to free-text reports in NSCLC.
Keywords: Lung; Non-small-cell lung carcinoma; PET-CT; TNM classification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.K. is a member of the speakers’s bureau of Siemens Healthineers. M.S.M. is a member of the speakers bureau of Siemens Healthineers. M.B. received consulting/speaker honoraria from Life Molecular Imaging, GE Healthcare, and Roche, and reader honoraria from Life Molecular Imaging. C.C.C. is on the speaker’s bureau for Brainlab AG and is on the advisory board of Siemens Healthineers. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen RD, Vils Pedersen MR, Hesseldal L, Rafaelsen SR (2023) Using structured templates or free text style in reporting CT staging on colon cancer: a national survey. Acta Radiol 64:1765–1769 - PubMed
-
- Dewey M, Bosserdt M, Dodd JD, Thun S, Kressel HY (2019) Clinical imaging research: higher evidence, global collaboration, improved reporting, and data sharing are the grand challenges. Radiology 291:547–552 - PubMed
-
- Dobranowski J, Sommer W (2019) Structured radiology reporting: addressing the communication quality gap. SN Compr Clin Med 1:397–407
-
- Flusberg M, Ganeles J, Ekinci T et al (2017) Impact of a structured report template on the quality of CT and MRI reports for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis. J Am Coll Radiol 14:1206–1211 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

