Early Intervention in Patients With Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis and Myocardial Fibrosis: The EVOLVED Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 39466640
- PMCID: PMC11519785
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2024.22730
Early Intervention in Patients With Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis and Myocardial Fibrosis: The EVOLVED Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Development of myocardial fibrosis in patients with aortic stenosis precedes left ventricular decompensation and is associated with an adverse long-term prognosis.
Objective: To investigate whether early valve intervention reduced the incidence of all-cause death or unplanned aortic stenosis-related hospitalization in asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis and myocardial fibrosis.
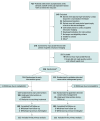
Design, setting, and participants: This prospective, randomized, open-label, masked end point trial was conducted between August 2017 and October 2022 at 24 cardiac centers across the UK and Australia. Asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis and myocardial fibrosis were included. The final date of follow-up was July 26, 2024.
Intervention: Early valve intervention with transcatheter or surgical aortic valve replacement or guideline-directed conservative management.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause death or unplanned aortic stenosis-related hospitalization in a time-to-first-event intention-to-treat analysis. There were 9 secondary outcomes, including the components of the primary outcome and symptom status at 12 months.
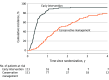
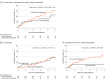
Results: The trial enrolled 224 eligible patients (mean [SD] age, 73 [9] years; 63 women [28%]; mean [SD] aortic valve peak velocity of 4.3 [0.5] m/s) of the originally planned sample size of 356 patients. The primary end point occurred in 20 of 113 patients (18%) in the early intervention group and 25 of 111 patients (23%) in the guideline-directed conservative management group (hazard ratio, 0.79 [95% CI, 0.44-1.43]; P = .44; between-group difference, -4.82% [95% CI, -15.31% to 5.66%]). Of 9 prespecified secondary end points, 7 showed no significant difference. All-cause death occurred in 16 of 113 patients (14%) in the early intervention group and 14 of 111 (13%) in the guideline-directed group (hazard ratio, 1.22 [95% CI, 0.59-2.51]) and unplanned aortic stenosis hospitalization occurred in 7 of 113 patients (6%) and 19 of 111 patients (17%), respectively (hazard ratio, 0.37 [95% CI, 0.16-0.88]). Early intervention was associated with a lower 12-month rate of New York Heart Association class II-IV symptoms than guideline-directed conservative management (21 [19.7%] vs 39 [37.9%]; odds ratio, 0.37 [95% CI, 0.20-0.70]).
Conclusions and relevance: In asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis and myocardial fibrosis, early aortic valve intervention had no demonstrable effect on all-cause death or unplanned aortic stenosis-related hospitalization. The trial had a wide 95% CI around the primary end point, with further research needed to confirm these findings.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03094143.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
Myocardial Fibrosis and Timing of Intervention for Aortic Stenosis.JAMA. 2025 Jan 21;333(3):207-209. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.22853. JAMA. 2025. PMID: 39466632 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vahanian A, Beyersdorf F, Praz F, et al. ; ESC/EACTS Scientific Document Group . 2021 ESC/EACTS guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(7):561-632. - PubMed
-
- Otto CM, Nishimura RA, Bonow RO, et al. 2020 ACC/AHA guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021;143(5):e72-e227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

